What Is LED Polarity and Why Does It Matter? LED polarity is one of the most important things to understand when working with LEDs, especilly in PCB assembly. A wrong LED polarity put will cause the failure of the PCB product. Unlike regular bulbs, LEDs only work if they are connected the right way. If you mix up the positive and negative sides, the LED won’t light up. So, whether you’re building a simple LED circuit, installing LED light strips, or working with surface-mount LEDs, understanding LED polarity helps prevent issues. In this guide, we’ll answer the most common questions about LED polarity and explain how to identify and test LED connections correctly.

What Is LED Polarity?
LED polarity refers to the direction in which an LED must be connected to a power source. Since LEDs are diodes, they allow current to flow in only one direction. This means that one leg of the LED must be connected to the positive side of the power supply, while the other must go to the negative side.
Each LED has two legs:
- Anode (+): This is the positive leg. It needs to be connected to the positive terminal of the power source.
- Cathode (-): This is the negative leg. It must connect to the negative terminal.
If the LED is wired incorrectly, it won’t light up because no current will flow through it. Some LEDs may even get damaged if too much voltage is applied in the wrong direction.
Do LEDs Have Polarity?
Yes, LEDs have polarity, and they must be connected correctly to function. Unlike traditional incandescent bulbs that work regardless of connection direction, LEDs only operate when the anode is connected to the positive voltage and the cathode to the ground.
The reason for this is that LEDs are light-emitting diodes. Diodes are semiconductor components that allow current to pass in one direction while blocking it in the other. When you reverse the polarity of an LED, it stops conducting electricity, which means it won’t produce light.
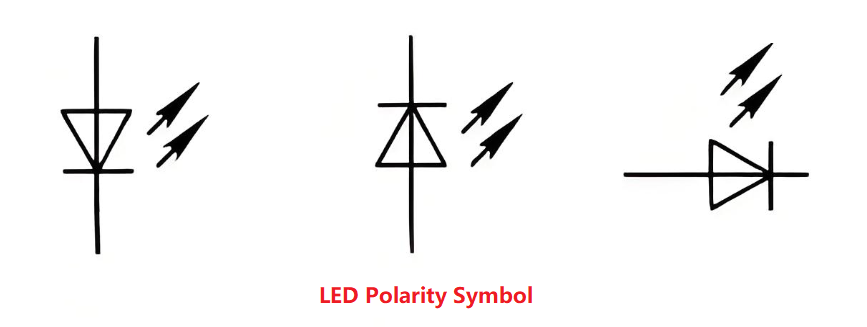
LED Polarity Symbol
If you look at circuit diagrams, you’ll notice a special symbol used for LEDs. The LED polarity symbol is similar to a regular diode symbol but has two arrows pointing away from it to indicate light emission. Below are the common led polarity symbols used in the industry:
Are LED Light Bulbs Polarity Sensitive?
It depends on the type of LED light bulb.
- AC-powered LED bulbs (like household LED light bulbs) are usually not polarity sensitive because they contain internal rectifiers that convert AC to DC.
- DC-powered LEDs (such as those used in automotive applications, flashlights, or indicator lights) are polarity sensitive and will not work if connected incorrectly.
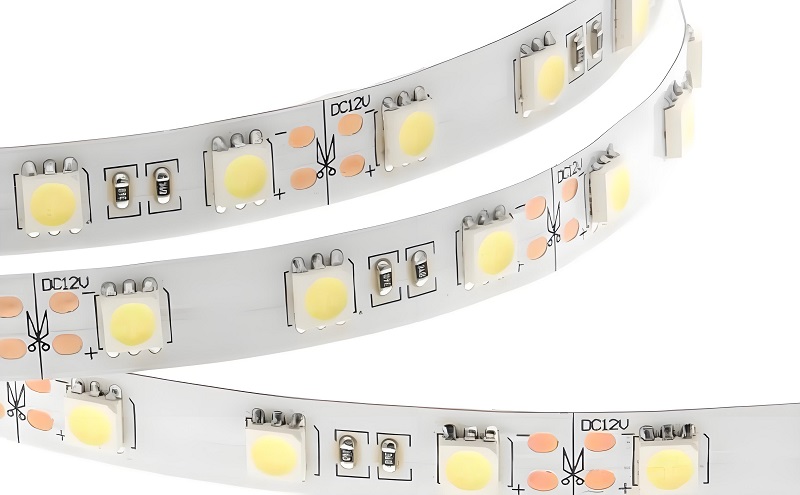
When working with DC-powered LED systems, checking the wiring is crucial. Many LED strips and car LEDs have markings to indicate which side should connect to positive and which should go to negative.
How Do You Identify the Polarity of an LED?
There are several ways to determine LED polarity:
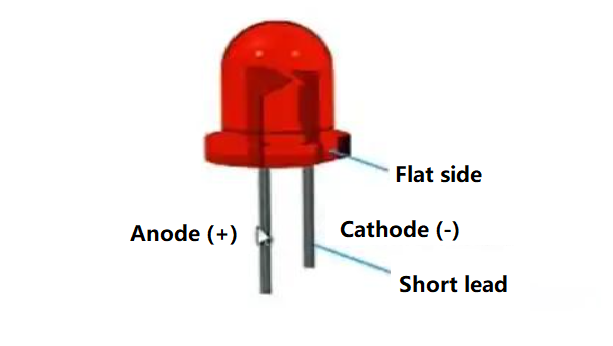
1. Check the Lead Length
If it has leds, check the lead length is the most important method to identify:
- The longer lead is the anode (+).
- The shorter lead is the cathode (-).
This method works well for new LEDs, but if the leads are trimmed, other methods may be needed.
2. Look for a Flat Edge
On many through-hole LEDs, the cathode side has a flat edge on the plastic casing. This marking helps quickly identify polarity. (Please refer above images of LED).
3. Inspect the Internal Structure
If you have a clear LED, you can look inside:
- The larger internal piece is usually the cathode (-).
- The smaller piece is the anode (+).
This method works well for transparent or diffused LEDs but is harder for small surface-mount LEDs.
4. Use a Multimeter
A digital multimeter with a diode test function can confirm polarity. When the red probe touches the anode and the black probe touches the cathode, the LED will glow slightly or show a voltage reading. If no reading appears, reverse the probes.
What Happens If LED Polarity Is Reversed?
If the LED is connected backward, it won’t light up. Unlike incandescent bulbs, which work in either direction, LEDs only allow current to flow in one way. Here are some common issues if LED polarity is reversed:
1. No Light Emission: Since LEDs are polarized components, they only work when connected correctly. If the polarity is reversed, current cannot flow, and the LED will not light up.
2. Potential Damage: In some cases, a reversed connection may cause damage. Excessive reverse voltage or current can harm the internal structure of the LED.
3. Overheating: Incorrect polarity may lead to improper current flow, generating excess heat. This can affect both the LED and nearby circuit components.
4. Short Circuit Risk: A severe polarity reversal could create a short circuit, which may harm the power source or other connected components.
5. Unstable Lighting: In rare cases, an incorrectly wired LED may flicker or dim unpredictably instead of staying off completely.
In most cases, a reversed LED will not get damaged unless the voltage is too high. However, some circuits use protection resistors or diodes to prevent issues caused by incorrect polarity.
Does LED Polarity Matter?
Yes, LED polarity matters because LEDs are diodes that function only when connected correctly. If you ignore polarity, the LED won’t work. In some cases, incorrect wiring can cause damage, especially in high-power LEDs or integrated circuits.
To avoid problems:
- Always check the polarity markings before connecting an LED.
- Use a multimeter if unsure.
- Follow circuit diagrams carefully.
How to Check an LED with a Multimeter?
Using a multimeter is one of the easiest ways to test an LED’s polarity and functionality. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Set the Multimeter to Diode Test Mode
Most digital multimeters have a diode test mode, usually marked with a diode symbol (a triangle pointing to a line). If your multimeter doesn’t have this mode, use the resistance (Ω) setting on the lowest range.
2. Identify the Probes
- The red probe is the positive (+) lead.
- The black probe is the negative (-) lead.
3. Connect the Probes to the LED Legs
Touch the red probe to one leg and the black probe to the other.
- If the LED lights up faintly or shows a voltage reading (typically 1.8V to 3.5V, depending on the LED type), the red probe is on the anode (+), and the black probe is on the cathode (-).
- If nothing happens, swap the probes and try again.
4. Interpret the Results
- If the LED lights up, it means it is working, and you have identified the correct polarity.
- If the LED doesn’t light up in either direction, it may be faulty or burned out.
- If using the resistance mode, a working LED will show a resistance value in one direction and an infinite resistance (OL) in the other.
5. Testing Surface-Mount LEDs (SMD LEDs)
Since SMD LEDs are small and lack long leads, identifying polarity can be tricky. Many have a small marking on the cathode side. To test them:
- Use fine-tip multimeter probes.
- Hold the probes gently on the pads.
- Observe if the LED lights up or if a voltage reading appears.
A multimeter is a quick and reliable tool to check LED polarity before installing it in a circuit.
Which Side of the LED Should You Put a Resistor?
A resistor is needed to control current flow and protect the LED. The resistor can go on either side of the LED—anode or cathode—without affecting polarity. However, placing it on the anode side (+) is common for consistency in circuit designs.
Without a resistor, the LED might receive too much current, which could shorten its lifespan or cause it to burn out.
FAQs
1. Can LED polarity be ignored?
No, LED polarity is essential for proper operation. If wired incorrectly, the LED will not work.
2. Do surface-mount LEDs have polarity?
Yes, surface-mount LEDs have polarity. Manufacturers usually mark the cathode with a dot or a line.
3. What happens if an LED is connected to AC power?
An LED without a rectifier will flicker or not work properly on AC power. A rectifier or resistor is needed for AC operation.
4. How do I fix a reversed LED?
Simply swap the connections. If the LED hasn’t been damaged, it should work fine.
5. Why do some LEDs have built-in resistors?
Built-in resistors simplify wiring by ensuring safe current levels. These LEDs can be directly connected to power sources without extra components.