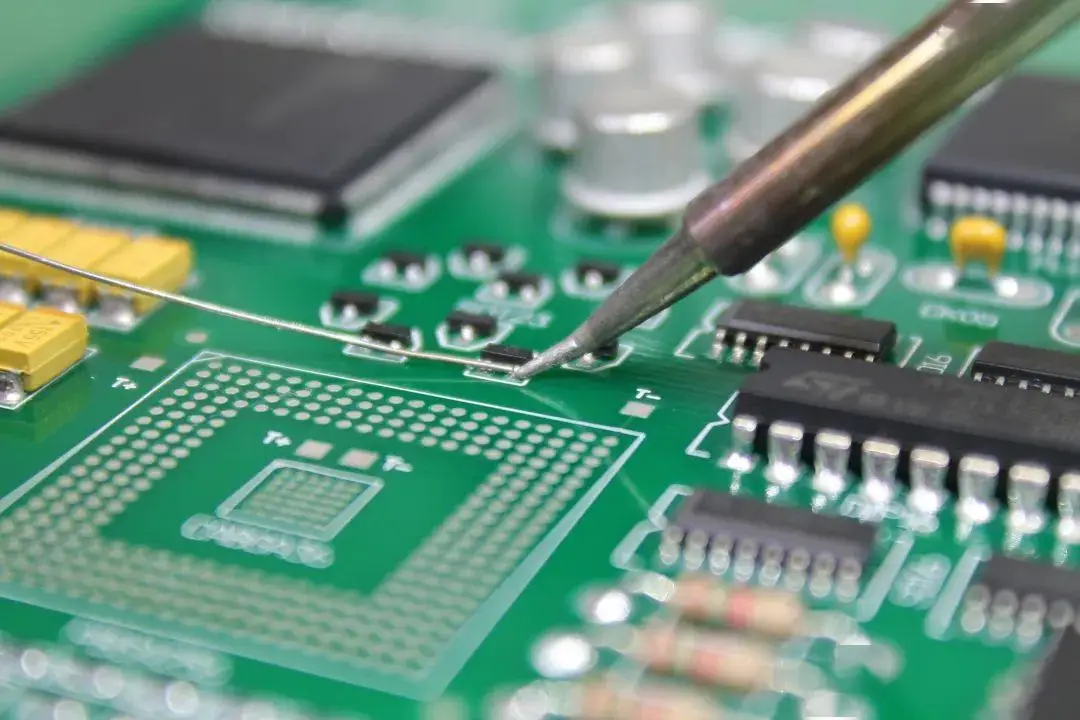
In PCB design, you’ll often notice rows of small holes along the edges of PCB panels. These holes, which looks like bit by a mouse, are commonly referred to as mouse bites PCB. They are also known as stamped vias or stamp holes due to their resemblance to the perforations found on postage stamps. These holes play a crucial role in securing components and establishing connections within the PCB, particularly during the breakaway process, where multiple PCBs are separated from a larger panel.
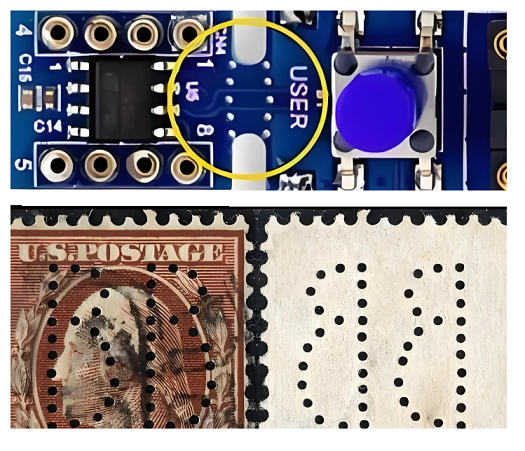
What is Mouse Bite in PCB?
What is mouse bites PCB? In the PCB world, a mouse bite refers to a small hole or notch created at the edges of the PCB panel. These notches are used to facilitate the separation of individual boards from the panel. The term “mouse bite” comes from the small, round shape of the indentation, resembling a tiny “bite” taken out of the PCB. The notches are typically placed along the edges of the PCB during the manufacturing process and are especially useful in high-volume production, where multiple PCBs are often manufactured as part of a larger panel.
Purpose of PCB Mouse Bites
The primary purpose of mouse bites in PCB design is to assist in the breakaway process. During the manufacturing of PCBs, multiple boards are often produced in a single panel. After fabrication, these panels must be separated into individual PCBs. Without a proper method, separating them could result in damage to the boards or pose a risk to delicate components.
Mouse bites are engineered to provide a controlled, predictable break. When the panel is ready for separation, the notches help to guide the break and reduce the chance of fractures or warping. Additionally, mouse bites are essential in panels where the PCBs are tightly packed, ensuring the separation process remains smooth and efficient.
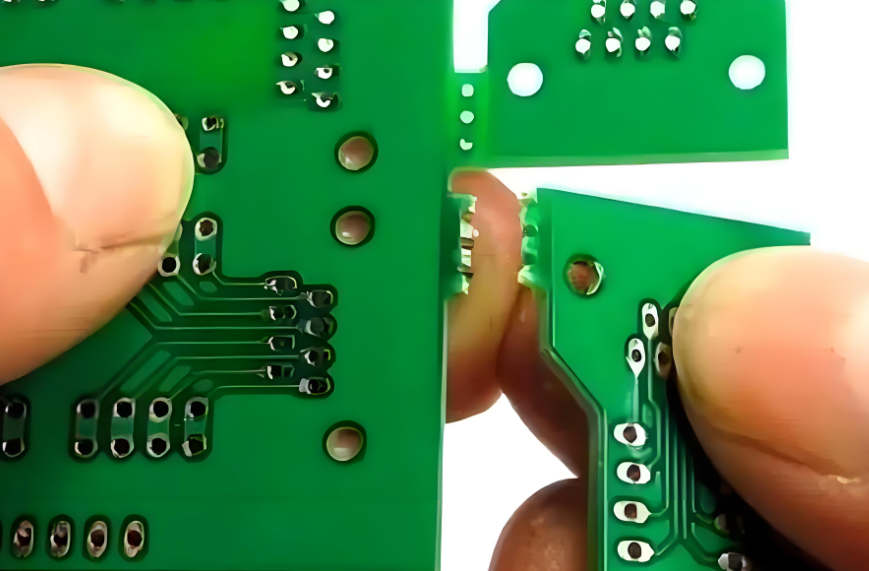
Advantages of Mouse Bite in PCB
There are several notable advantages to using mouse bites in PCB design:
- Controlled Separation: Mouse bites provide a controlled break, minimizing the risk of damaging the PCB during the separation process. They guide the break and ensure that it occurs where it’s most needed.
- Improved Efficiency: Adding mouse bites to a PCB panel significantly speeds up the manufacturing process. This allows for quicker breakaway times, resulting in more efficient production cycles.
- Cost-Effective: By reducing the likelihood of breakage or errors, mouse bites save money on rework, damaged boards, or production delays.
- Design Flexibility: Mouse bites are particularly beneficial when manufacturing smaller PCBs within a larger panel. They offer design flexibility without compromising the integrity of the individual boards.
How Do You Add Mouse Bites to PCB?
Adding mouse bites to a PCB design is typically done in the design phase. The process involves creating small circular notches along the edges of the PCB. These notches are strategically placed where separation is intended.
To add mouse bites in PCB design software, follow these steps. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to place mouse bites in Altium Designer:
1. Open Your PCB Project
Start Altium Designer and open the PCB project that you’re working on.
2. Create or Edit the PCB Panel
If you’re working with a multi-board panel, go to Design > Define Board Shape to create or edit the panel where you want to add the mouse bites.
3. Set Up the Mouse Bite Tool
In Altium Designer, go to the Tools menu and select Create Polygon Pour. This tool can be used to make the necessary notches (mouse bites) along the edges of the PCB.
4. Select the Edge of the PCB
With the polygon pour tool activated, click along the edge of the PCB where you want the mouse bites to appear.
5. Define the Hole Parameters
Define the size and shape of the mouse bite by adjusting the hole diameter and spacing. Mouse bites are typically circular, and you can customize the hole size to fit your design requirements (e.g., 0.3mm to 1.2mm).
6. Place the Mouse Bites
Position the mouse bites along the edges of the panel. Make sure the notches are evenly spaced and aligned according to your design rules.
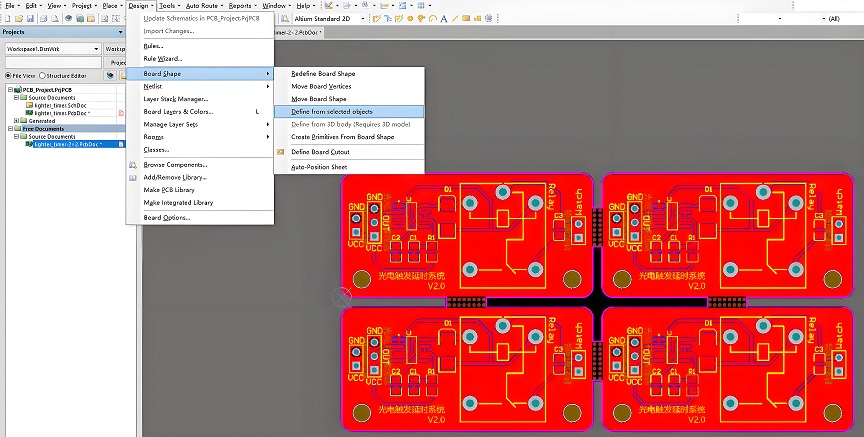
7. Ensure Proper Clearance
Verify that there is enough clearance from the PCB edges (at least 0.3mm) to avoid damage or cracking during separation.
8. Check the Design Rules
Review your Design Rules to ensure the mouse bites meet the necessary standards for the board’s separation and manufacturing process.
9. Save the Design
Once you’re satisfied with the placement and spacing, save your design.
10. Export the Files
After placing the mouse bites, export your Gerber files for manufacturing by going to File > Fabrication Outputs and selecting the appropriate output format.
By following these steps, you can efficiently place mouse bites in your PCB design using Altium Designer. If you are not familiar with Altium software, you are welcome to contact Best Technology team, we offer free technical support for our customers.
What Is the Difference Between V-Groove and Mouse Bites?
Both V-groove and mouse bites are methods used to separate PCBs after fabrication, but there are some key differences between the two:
V-Groove
V-grooves are deeper cuts, often formed by a mechanical process that creates a “V” shape along the edge of the PCB. This type of break is typically used for larger panels and requires additional precision during manufacturing.
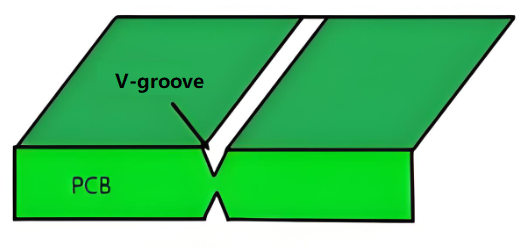
- Pros: High precision, smooth cutting surface, suitable for automated production, and aesthetically pleasing. It is ideal for applications with strict precision requirements.
- Cons: The edge strength is relatively low, making it unsuitable for applications that need to endure high mechanical stress. For PCBs with more than a certain number of layers, controlling the V-groove depth becomes more challenging, potentially affecting product quality.
Mouse Bites
Mouse bites are used as a method for inter-layer connections within multi-layer PCBs, especially in high-density interconnect (HDI) designs. Small, deep holes are drilled between the layers of the PCB, and copper is plated on the hole walls to create electrical connections between layers.

- Pros: High space utilization, especially suitable for compact designs. It improves signal transmission performance by reducing signal delay and cross-talk. It is suitable for more complex multi-layer board designs.
- Cons: The manufacturing process is complex and costly. It requires high precision in design and testing, increasing development difficulty.
Tips for Selecting the Right PCB Breakaway Method
Choosing the correct breakaway method is crucial for ensuring your PCBs are separated cleanly and efficiently. Here are some tips to consider:
- Panel Size: Larger panels may benefit from V-grooves, while smaller or more delicate boards are better suited for mouse bites.
- Design Considerations: If your design has sensitive components near the edge, mouse bites may be a better option since they cause less stress to the board during separation.
- Cost and Efficiency: Mouse bites are typically more cost-effective for smaller runs, while V-grooves may be better for high-volume production.
Design Guide for Mouse Bites PCB
The design rules for mouse bites are critical for ensuring the reliability and stability of the PCB. Below are the requirements for the design rules of stamped holes in PCBs:
1. Hole Diameter: The diameter of the mouse bites should be selected based on the design requirements and the connected components. Typically, common hole sizes range from 0.3mm to 1.2mm.
2. Edge Clearance: To ensure that the hole has enough distance from the PCB edge and avoid cracking or peeling, the design rules require a minimum clearance of 0.3mm from the edge.
3. Hole Layout: The layout of the holes in PCB design is crucial. Holes should be distributed more concentrically and evenly across the PCB to avoid overcrowding, ensuring the stability and reliability of connections.
4. Hole Reinforcement: Certain components, such as resistors and capacitors, may loosen due to mechanical shock or vibration. To increase stability, design rules require the presence of pads or filling rings around the mouse bites hole to enhance the connection’s sturdiness.
5. Pad Size: To ensure welding quality and reliability, the mouse bites should be paired with a sufficiently large pad. The pad’s diameter is generally at least twice the hole size, ensuring ample space during the soldering process.
6. Trace Routing: To maintain the electrical performance and stability of the mouse bites, traces should avoid passing directly through the hole whenever possible. If traces must pass through the hole, they should not intersect with pins, and dead zones should be avoided.
7. Trace Spacing: To prevent interference between traces and avoid soldering errors, the design rules require sufficient trace spacing between stamped holes.
FAQs
Q1: Can I use mouse bites in all PCB designs?
Yes, mouse bites are ideal for most PCB designs that need to be separated after manufacturing. However, they are best suited for smaller boards or those with less sensitive components along the edges.
Q2: How do I avoid damaging my PCB during the separation process?
By using mouse bites or V-grooves, you can reduce the risk of damaging your PCB. Properly designed notches ensure a controlled break, which minimizes the risk of cracks or fractures.
Q3: Are mouse bites more cost-effective than V-grooves?
Yes, mouse bites are generally more affordable than V-grooves, especially for smaller production runs.
Q4: Can mouse bites be placed on the entire PCB edge?
Yes, mouse bites can be placed along the entire edge of the PCB, but it’s important to leave enough margin from the board’s edge to prevent cracks or damage.
Q5: How do mouse bites differ from traditional breakaway tabs?
Mouse bites create small perforations that guide the break along the PCB’s edge, while traditional breakaway tabs usually involve larger cuts or slots. Mouse bites provide more precise separation with less risk of board damage.