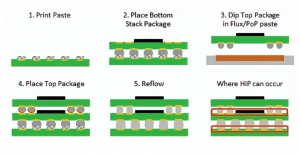
Definition of Solder Paste Flux
Solder paste flux is a material used in the field of electronic welding, usually consisting of tin, silver, copper, nickel and other metal powders as well as flux and solvent components. It divided into clean flux and no clean flux. It can form a thin layer of solder paste on the surface of the circuit board, which has strong adhesion and electrical conductivity, and can make electronic components and circuit boards quickly welded together. The ingredients of solder paste flux include:
- Solvent: Used to dissolve solid or liquid components and regulate uniformity.
- Resin: Increase the adhesion of solder paste, prevent PCB reoxidation after welding.
- Activator: Remove oxidized substances from the through hole surface layer of PCB copper film and parts SMT patch, reduce the liquid surface tension of tin and lead.
- Thixotropic agent: Adjust the viscosity of solder paste to prevent tailing and adhesion.
There are two common solder paste flux types used in the PCB assembly:
- Water-soluble flux: large solubility, strong activity, residue after welding can be cleaned with water. It also called cleaned flux.
- No-cleaning flux: little residue after welding, non-toxic and tasteless, does not pollute the environment.

No Clean Flux vs. Clean Flux
When working with PCBs, the choice between no clean flux and clean flux can greatly impact the quality, reliability, and cost of the final product. Understanding their properties, benefits, and appropriate use cases helps in making informed decisions for different soldering scenarios.
Composition and Characteristics
Clean Flux: This type of flux contains active ingredients designed to ensure thorough cleaning during the soldering process. Its composition includes stronger activators that effectively remove oxides and contaminants from the metal surfaces being soldered. However, the resulting residue left behind is often corrosive or conductive. Thus, it must be cleaned after soldering to prevent damage to the circuit or degradation of electrical performance.
No Clean Flux: As its name implies, no clean flux is formulated to leave minimal, non-corrosive, and non-conductive residue. The formulation uses milder activators that still assist in the soldering process but are designed to burn off or remain as safe deposits. These residues do not interfere with the circuit’s electrical properties, allowing the assembly to be used without further cleaning. The residue left is typically clear and dry, posing minimal risk under normal conditions.
Performance and Suitability
Clean Flux is ideal for applications that demand high reliability and minimal contamination. Examples include:
- High-frequency circuits: Residue from clean flux can interfere with signal integrity. Removing these residues ensures optimal performance.
- Sensitive electronic devices: Medical devices or aerospace electronics that operate in critical conditions benefit from using clean flux due to the necessity of pristine circuit conditions.
No Clean Flux, on the other hand, is suited for:
- Consumer electronics: Phones, computers, and household gadgets that do not operate under extreme conditions.
- Cost-sensitive production: Mass production benefits from the time and expense saved by eliminating the cleaning step.
- Environmentally conscious manufacturing: With no post-soldering cleaning required, the use of chemical solvents is minimized.
Clean Flux Advantages:
Superior Cleanliness: Ensures there is no residue to attract moisture or create pathways for current leakage.
Reliability in Critical Applications: Guarantees circuits remain in top condition, preventing issues in high-risk environments.
Certification Compliance: Many stringent industry standards and certifications require flux to be cleaned for safety and performance assurance.
Disadvantages of Clean Flux:
Additional Steps: Post-soldering cleaning adds time, labor, and costs.
Environmental Impact: Cleaning often involves chemical solvents that must be disposed of properly.
Equipment Needs: Special machinery like ultrasonic cleaners may be required to remove flux residues effectively.
No Clean Flux Advantages:
Time and Cost Savings: Speeds up the production process by eliminating the need for cleaning.
Reduced Chemical Use: Contributes to a cleaner manufacturing process by avoiding harsh cleaning agents.
Simplified Workflow: Reduces the complexity of production lines by removing an extra step.
Disadvantages of No Clean Flux:
Limited High-Reliability Use: In high-frequency or high-voltage circuits, even minimal residue could pose potential risks.
Residue Visibility: While safe, residues can still be visible, which might not be acceptable for circuits requiring visual inspection.
Selective Suitability: Not ideal for all applications, especially those where long-term exposure to various environmental factors could react with even benign residues.
Application Considerations
Clean Flux is the better choice when:
The circuit board is part of a medical device, aerospace system, or any application where safety and precision are crucial.
The project involves sensitive circuits that cannot tolerate any contaminants, no matter how minimal.
Certification bodies require absolute cleanliness for approval.
No Clean Flux is more suitable when:
Production efficiency is a priority, as in consumer electronics manufacturing.
The board does not require visual perfection or meets the tolerance for low-level residues.
Environmental policies favor reduced chemical use and waste.
Why is it Called No Clean Flux?
The term no clean flux reflects its primary feature: no mandatory post-soldering cleaning. This type of flux is made with a formulation that leaves behind minimal, safe residues. The composition typically includes a mix of weak organic acids and solvents that burn off or leave a thin, inert layer during the soldering process. This layer is non-conductive and won’t affect the circuit’s performance, eliminating the need for additional cleaning steps.
This type of flux gained popularity as manufacturing practices evolved to become faster and more cost-efficient. The avoidance of cleaning also means fewer chemicals are used, supporting environmentally friendly production lines. The convenience of no clean flux does not compromise soldering quality in most cases, making it a go-to choice for many electronics manufacturers.
What Happens if You Don’t Clean Flux on a PCBA?
Not cleaning the flux on the PCBA can cause a range of problems including reduced electrical performance, corrosion, leakage, short circuit, etc.
First of all, incomplete flux cleaning can significantly reduce the electrical performance of the circuit. Residual flux may cause resistance to increase, capacitance to decrease, and in severe cases, complete circuit failure. In addition, residual flux may cause metal corrosion and leakage, increasing the risk of circuit damage and short circuit. Improper cleaning will also affect the insulation performance of the circuit, resulting in reduced insulation impedance, which may cause leakage or more serious circuit failure.
When the temperature changes, the flux residue may also cause the thermal expansion mismatch between the solder joint and the circuit board, causing the solder joint to crack or fall off, and eventually lead to circuit failure. In addition, the residual flux may form electron movement during electrification, resulting in short circuit and product failure . Especially in modern electronic products, the pad spacing is getting smaller and smaller, and the presence of residue increases the possibility of short circuit.
When to Use No Clean Flux?
No clean flux fits well with everyday consumer electronics, where quick production and cost savings are key. It is useful for circuits where non-conductive residue won’t impact performance, like in standard home appliances or low-sensitivity equipment. Some typical situations are suitable to use no-clean flux, like:
- Environment with very low requirements for residue after soldering: no-clean flux has very little residue after welding, and can reach the standard of ionic cleanliness without cleaning. It is suitable for environments with very high requirements for residue after welding.
- Occasions with high environmental requirements : no-cleaning flux does not contain halide active agent, no need to clean, reduce the discharge of waste gas and wastewater, in line with the requirements of environmental protection.
- Project requires high economic benefit: the use of no-cleaning flux can reduce the input of cleaning equipment and cleaning solvent, reduce the production cost.
- Low odor requirements situation: the traditional loose-scented flux has a larger odor, while the no-clean flux has a smaller odor. It is suitable for the environment with low odor requirements.
How to Use No Clean Flux Paste?
The basic steps for using no-clean flux are as follows:
1. Clean the welding part: Before using the flux, clean the welding part to ensure that there is no oil, degreaser or moisture on the surface to avoid affecting the welding effect and welding strength
2. Apply flux: After stirring the no-clean flux evenly, apply the flux on the welding part by brushing or dripping, and ensure that the coverage area is sufficient
3. Welding: After waiting for a while, you can perform normal welding. The function of the flux is to improve the welding quality and make the contact surface of the electronic components easy to melt during the welding process.
Precautions during use:
1. Environmental requirements: No-clean flux is a flammable chemical material. It should be operated in a well-ventilated environment, away from fire and avoid direct sunlight
2. Storage and replacement: The opened flux should be sealed before storage. Do not pour the used flux back into the original packaging to ensure the cleanliness of the original liquid. The flux should be replaced with new liquid after 50 hours of use to prevent contamination, aging and degradation that affect the work effect and quality.
3. Safe handling: The scrapped flux must be handled by a dedicated person and must not be dumped at will to pollute the environment. If it is accidentally contaminated on your hands and feet, rinse it immediately with soap and water; if it is contaminated on your face, rinse it immediately with soap and water. If the situation is serious, seek medical treatment.
Best Technology engaging in PCB and PCBA assembly industry for more than 18 years. We have professional engineering team to offer one-to-one technical support. And all of our core members have over 10 years experience in PCB industry, we are so confident that we can serve you perfect! Contact us for more!