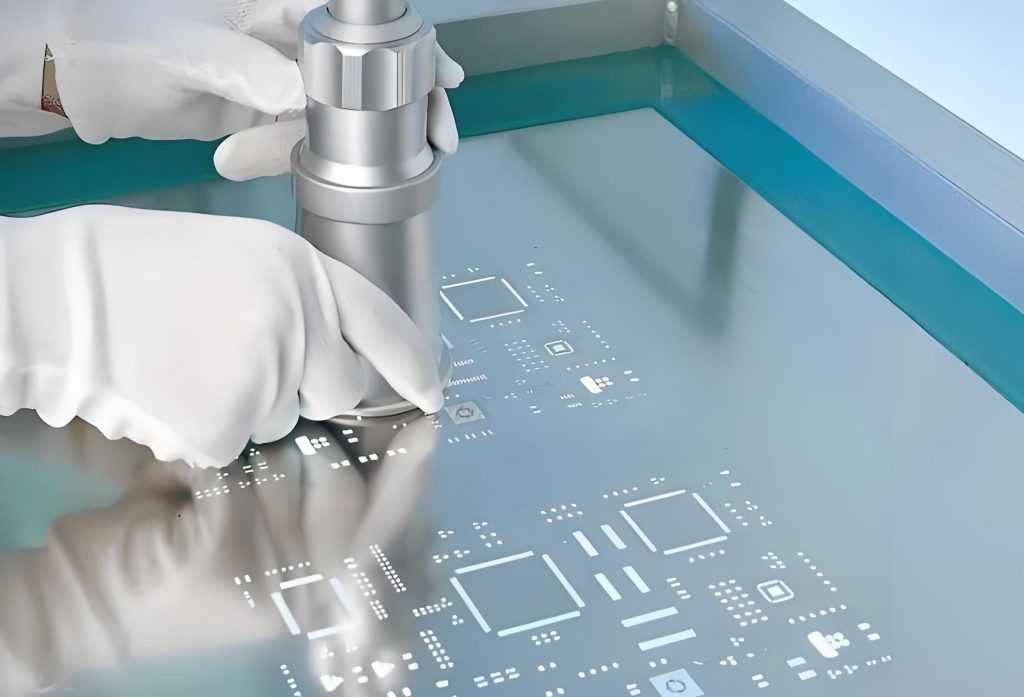
What is a Stencil in PCB?
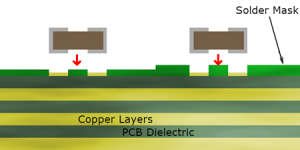
A PCB stencil is a precision tool used in the process of assembling printed circuit boards. Its main function is to apply solder paste to the board in a controlled manner, ensuring the paste only reaches the pads where components will be mounted. By creating uniform paste deposits, the stencil facilitates the correct soldering of components during the assembly process, contributing significantly to the quality and reliability of the final product.

What Does a Stencil Do?
A PCB stencil plays several crucial roles in the PCB assembly process, including:
1. Applies Solder Paste: The primary function of a stencil is to accurately apply solder paste to the PCB. The paste is deposited onto the pads of the PCB through the openings in the stencil, ensuring the right amount of paste is used for each component.
2. Improve Precision: By using a stencil, manufacturers can achieve highly precise solder paste placement. This is especially important for fine-pitch components, where precision is key to avoiding defects like bridging or insufficient solder.
3. High Efficiency: Stencils speed up the solder paste application process, making it more efficient than manual paste application. This is particularly beneficial in high-volume manufacturing, where consistency and speed are vital.
4. Reduces Human Error: Using a stencil minimizes the chances of human error in solder paste application. This leads to more consistent and reliable results, reducing the likelihood of defects in the final product.
5. Facilitates High-Volume Production: Stencils are essential for mass production, allowing manufacturers to quickly and efficiently apply paste across multiple PCBs with high consistency.
6. Improves Reflow Soldering: With the right amount of solder paste applied, the stencil helps ensure that the reflow soldering process is carried out effectively, leading to strong and durable solder joints.
What is a PCB Stencil Consist of?
A PCB stencil consists of several crucial components that work together to ensure precise solder paste application. These elements include:
1. Frame
The frame is essential for holding the stencil in place during the application process. It is categorized into movable frames and fixed frames. The movable frame attaches the steel plate directly to the frame, allowing the template to be reused. On the other hand, the fixed frame uses adhesive to attach the wire mesh to the formwork. For optimal performance, a strong frame with uniform steel tension—typically between 35 and 48 N/cm²—is preferred. The normal fixed frame tension is between 35 N to 42 N, ensuring stability and accuracy.
2. Sheet Plates
High-quality stainless steel plates such as 301/304 stainless steel are commonly used because they offer excellent mechanical properties, significantly increasing the service life of the stencil. Other materials such as copper plates, nickel alloy, and polyester may also be used, depending on the specific application requirements.
3. Mesh
The mesh is used to fix the steel plates and formwork in place. There are two main types of mesh: stainless steel mesh and polymer polyester mesh. Stainless steel mesh is typically around 100 mesh and ensures stable tension, but it can deform and lose tension over time. Polyester mesh, on the other hand, is made from an organic fabric that doesn’t easily deform and has a longer service life, making it a more durable option for long-term use.
4. Adhesive (Glue)
The glue used in PCB stencils serves as the binding material that attaches the trellis frame to the steel sheet. It is an essential part of maintaining the integrity and stability of the stencil. The adhesive used needs to provide strong adhesion and be able to withstand heavy cleaning with various plate cleaners without losing its effectiveness.
Together, these components—frame, sheet, mesh, and glue—combine to form a PCB stencil that ensures accurate, consistent, and efficient solder paste application during the PCB assembly process.
What Are the Different Types of Stencils?
There are various types of PCB stencils, each designed for specific applications and production requirements:
- Laser-Cut Stencils: These are the most accurate and commonly used type. Laser cutting provides high precision, making these stencils perfect for fine-pitch components or designs with intricate details.
- Etched Stencils: Etching is an older method but still used for simpler projects. Though less precise than laser-cut stencils, etched stencils are still valuable for projects where absolute precision is not as critical.
- 3D Printed Stencils: 3D printing technology has opened up a new avenue for creating PCB stencils. This method is ideal for low-volume or prototype PCB assembly, offering flexibility and faster turnaround times for custom designs.
- DIY Stencils: For hobbyists or small-scale production, DIY methods using materials like adhesive-backed foil or plastic sheets can be used to create simple stencils. These are cost-effective but come with trade-offs in precision and durability.
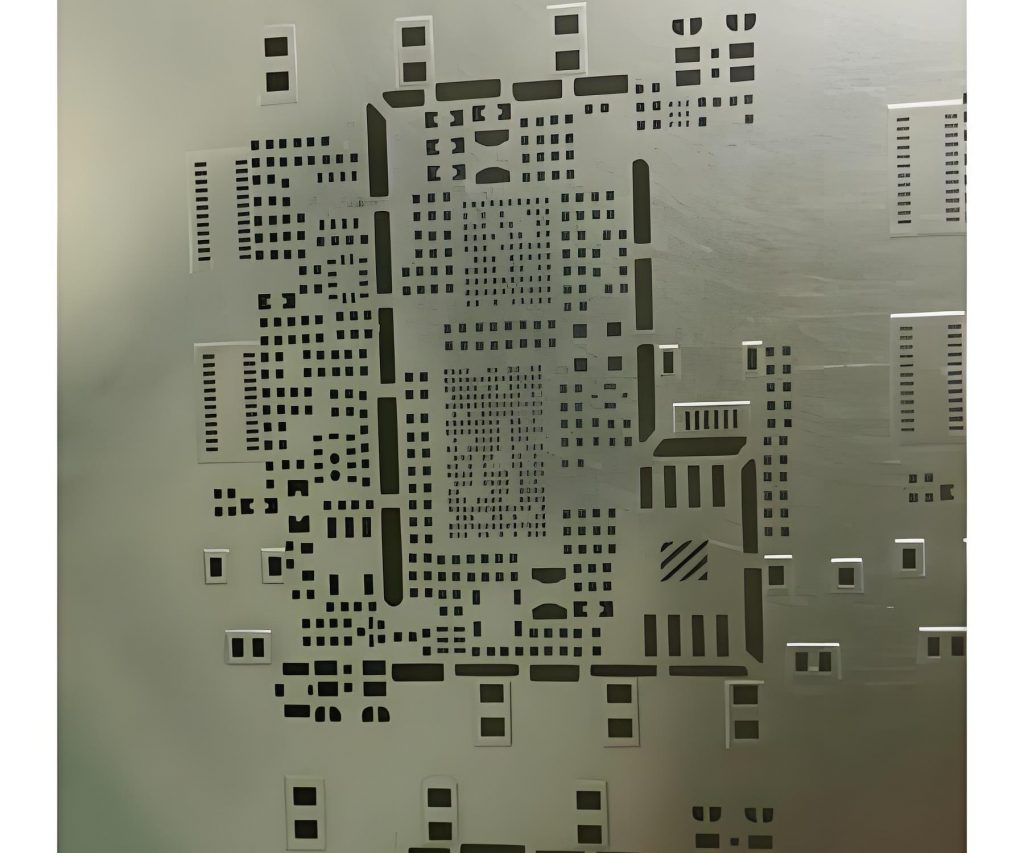
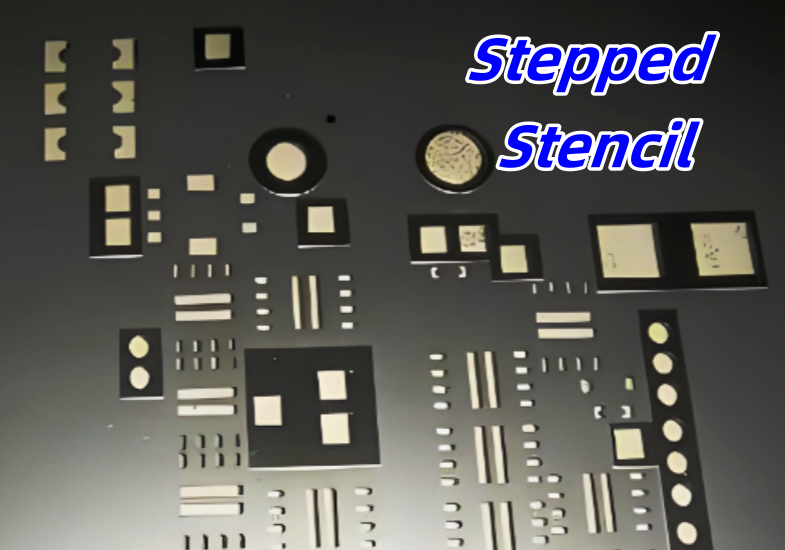
- Stepped Stencil: A stepped stencil features varying thicknesses across different areas of the stencil. These thickness changes, or “steps,” allow the stencil to deposit different amounts of solder paste for different components on the same PCB. Stepped stencils are particularly useful when there is a mix of fine-pitch components and larger, more spaced-out components on the same board. Below is a typical photo of stepped stencil.
PCB Stencil HS Code
The HS code for PCB stencils is 7314490000.
This code is specifically used for steel product, which includes PCB stencils used in the manufacturing process. It’s important to use the correct HS code for shipping and customs purposes to ensure smooth international transactions.
Warm Notice:
It’s always advisable to check with your local customs authority for any updates or specific requirements based on your region or the material type.
PCB Stencil Thickness
The thickness of a PCB stencil is an important factor in ensuring the correct amount of solder paste is applied. Generally, the stencil thickness ranges between 0.08 mm to 0.20 mm.
And it depends on the smallest spacing of the components on the PCB.
- For BGAs or ICs with a 0.35mm pitch, a stencil of 0.08mm or thinner is recommended. If the entire PCB features such fine-pitch components, a stencil thickness of 0.06mm or even 0.05mm is more suitable.
- For BGAs or ICs with a pitch of 0.4mm or greater, a 0.1mm thick stencil is acceptable. In some cases, for BGAs with a slightly larger pitch, a 0.08mm thick stencil may also be considered. When dealing with BGAs or ICs that have a pitch of 0.5mm or more, a 0.12mm thick stencil is the optimal choice.
Moreover, the stencil thickness affects both its suitability and lifespan. Thinner stencils, like 0.08mm, are ideal for high-precision solder points. On the other hand, thicker stencils, such as 0.12mm, are better for scenarios where component spacing is larger, ensuring greater stability and strength.
PCB Stencil Material
The material selection for PCB stencils influences the overall performance and durability of the tool. Common materials include:
- Stainless Steel: As the most popular option, stainless steel provides the necessary durability, resistance to corrosion, and ease of cleaning required for frequent use in high-precision environments.
- Nickel: While not as common as stainless steel, nickel-based stencils are valued for their flexibility and wear resistance. They are often chosen for specific applications requiring extra resilience.
The material selected must align with the type of PCB being produced, ensuring long-term effectiveness.
How to Make a PCB Stencil?
Creating a PCB stencil requires both precision and attention to detail. The process typically involves:
1. Designing the Stencil
The stencil design is created based on the PCB layout, ensuring the paste is applied to the correct pads.
2. Selecting the Material
Choose either stainless steel or nickel, depending on the project requirements.
3. Cutting or Etching the Design
For laser-cut stencils, a laser cutter is used to cut out the design with high precision. Etched stencils use chemical etching to create the openings.
4. Testing the Stencil
After the stencil is manufactured, it is tested to ensure that it meets the design specifications and can transfer solder paste accurately.
How Do You Solder a PCB with Stencils?
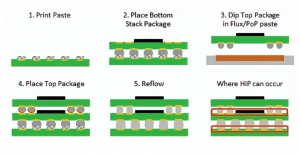
Soldering a PCB with a stencil involves several steps:
1. Place the PCB: The PCB is positioned on a flat surface or assembly board.
2. Align the Stencil: The PCB stencil is carefully placed on top of the PCB, ensuring that the openings align with the pads.
3. Apply Solder Paste: Solder paste is applied over the stencil using a squeegee or automated machine, filling the openings on the stencil.
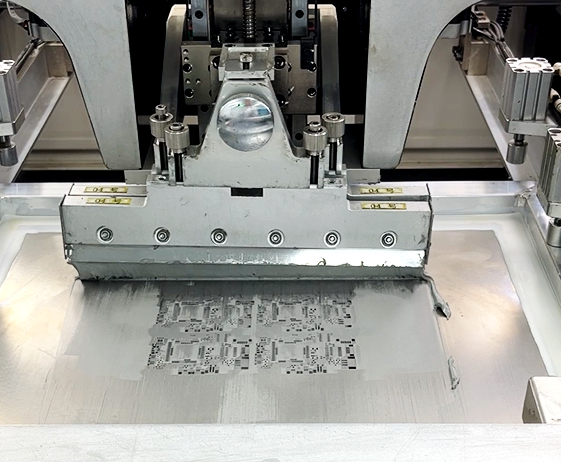

4. Remove the Stencil: The stencil is carefully lifted off, leaving solder paste on the pads.
5. Place Components: Components are placed onto the paste before the board is sent through a reflow oven, where the paste melts and creates strong, reliable solder joints.
How Much Does a PCB Stencil Cost?
The cost of a PCB stencil varies depending on the material, thickness, design complexity, and order volume. On average:
- Laser-cut stencils can range from $50 to $200 for single units, with bulk orders offering reduced prices.
- Etched stencils tend to be more affordable, typically priced around $30 to $100 depending on size and complexity.
- 3D printed stencils are generally more expensive due to the novelty of the technology, with prices starting around $100 for small projects.
For high-volume production, manufacturers often work with suppliers to negotiate bulk pricing.
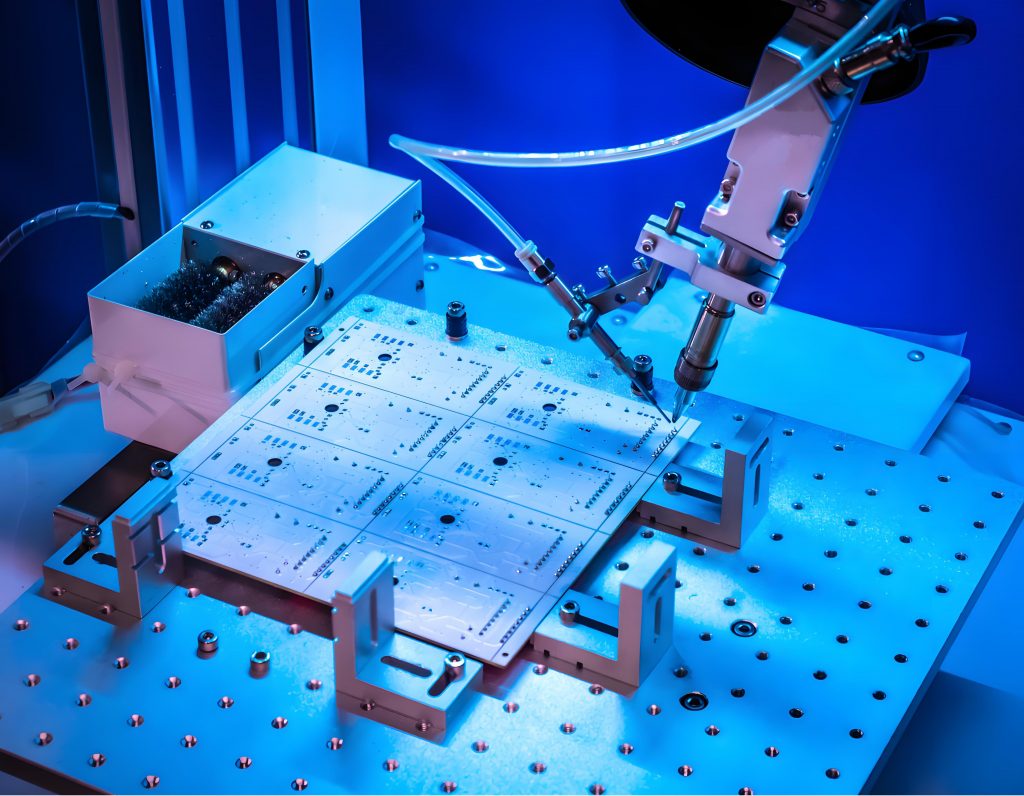
Stencil PCB Printers vs. PCB Stencils
While PCB stencils manually apply solder paste, PCB stencil printers are automated machines designed for mass production. The printer ensures the paste is applied consistently and accurately across the entire board, which is ideal for high-volume manufacturing.
The main difference is in automation. Stencil printers remove the need for manual labor, reducing the chance of human error and speeding up production time. On the other hand, manual PCB stencils are still effective for small-scale or custom PCB production, though they may require more time and care.
PCB Stencil Manufacturer – Best Technology
At Best Technology, we specialize in producing high-quality PCB stencils designed to meet the most demanding needs of the PCB assembly industry. With over 18 years of experience, we provide custom stencil solutions, ensuring your production runs smoothly and efficiently.
Whether you’re looking for a laser-cut, etched, or 3D printed stencil, our team offers precision and flexibility to help bring your designs to life. Choose Best Technology for your PCB stencil needs and experience the difference in quality and service. For more information, e-mail us at sales@bestpcbs.com.