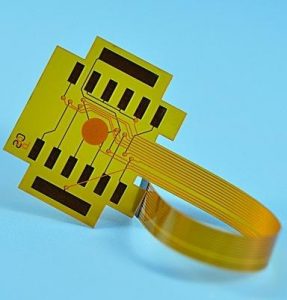
A high temperature resistant flexible PCB is a flexible printed circuit board that can maintain stable performance in a high temperature environment. It is usually composed of a flexible substrate, a conductive layer, and a cover layer. It has the characteristics of being bendable, foldable, and lightweight, and can withstand high temperatures without affecting its electrical and mechanical properties.
What is the maximum temperature for a flex PCB?
The high temperature resistance of a flexible PCB mainly depends on its substrate material. Generally speaking, the maximum temperature that a flexible PCB can withstand can reach 280 degrees in a short period of time, but the long-term temperature is generally between 120 degrees and 150 degrees. â
Different types of flexible PCB materials have different tolerances to temperature. PI is a commonly used flexible PCB substrate material that has excellent heat resistance and stability. It can maintain performance in the range of -200 degrees to 300 degrees, but the long-term use temperature is generally between 120 degrees and 150 degrees. â
In addition, the glass transition point of solder mask is about 110 degrees, so special attention should be paid to the temperature limit of these materials when designing flexible PCBs. â
What temperature should flexible PCB soldering be?
âThe optimal temperature range for flexible PCB soldering is 290-310 degrees Celsius. This temperature range is suitable for most flexible PCB soldering operations and can ensure soldering quality and component reliability.
In specific operations, the soldering time should be kept within a few seconds to prevent damage to the pads of the PCB board. Accurate temperature management is essential to ensure the solder joint quality and circuit performance of the PCB board. The soldering temperature may vary for different types of flexible PCBs.
What is high Tg PCB?
âHigh Tg PCB refers to PCB materials with higher glass transition temperature (Tg). â Tg is the temperature point at which the material changes from glass to rubber state. High Tg materials can still maintain good mechanical strength and dimensional stability at high temperatures. â
The main advantages of high Tg PCB include:
- âHeat resistanceâ: High Tg materials can still maintain good mechanical strength and dimensional stability at higher temperatures and are suitable for high temperature environments. â
- âMoisture resistanceâ: High Tg materials have low moisture absorption. Even after being heated after moisture absorption, they can maintain good mechanical strength and adhesion, reducing the risk of failure caused by moistureâ.
- âChemical resistanceâ: High Tg materials have better chemical stability at high temperatures and are not easy to decomposeâ.
- âDimensional stabilityâ: When the temperature changes, the dimensional changes of high Tg materials are small, ensuring the accuracy of PCBâ.
Application scenarios of high Tg PCB include:
- Lead-free manufacturing processâ: In highly functional and multi-layered electronic products, high Tg materials can ensure the stability and reliability of PCB in lead-free processesâ.
- âHigh temperature environmentâ: In applications that need to withstand high temperature environments, such as computers, mobile communication devices, etc., high Tg PCBs can ensure stable operation of the equipmentâ.
What are the disadvantages of flexible PCB?
The main disadvantages of flexible PCB include:
- âHigh one-time initial costâ: Since flexible PCBs are designed and manufactured for special applications, the initial circuit design, wiring and photographic plate costs are high.
- âDifficult to change and repairâ: Once a flexible PCB is made, it must be changed from the base map or the compiled photolithography program, so it is not easy to change. Its surface is covered with a protective film, which must be removed before repair and restored after repair, which is a more difficult taskâ.
How thick is the copper in a flex PCB?
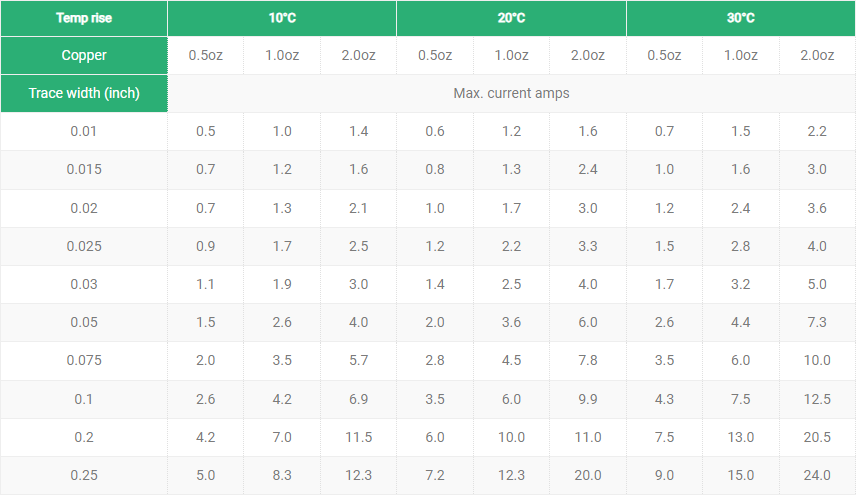
The copper foil thickness in a flexible PCB is usually around 0.1mm. The copper foil thickness of a flexible PCB is generally 0.1mm, which is one of its common specificationsâ.
In addition, the copper foil thickness of a rigid PCB has a wide range, and common thicknesses include 0.2mm, 0.4mm, 0.6mm, 0.8mm, 1.0mm, 1.2mm, 1.6mm, 2.0mm, etc.â. The copper foil thickness of a rigid PCB can be adjusted according to demand. For example, in an environment where high current and high power are required, the copper foil thickness may be higherâ.
Flexible PCB materials usually include polyester film, polyimide film, and fluorinated ethylene propylene film, etc. These materials are widely used in curved and flexible circuit designs in electronic devicesâ.
Why are Flex PCBs so expensive?
First, material cost is one of the main factors affecting the price of flexible PCBs. Flexible PCBs mainly use special materials such as polyimide (PI) and polyester film, which have excellent heat resistance and electrical properties, but are more expensive.
Second, manufacturing process is also an important reason for the high cost of flexible PCBs. The production process of flexible PCBs includes multiple complex links such as exposure, development, etching, lamination and testing. High-precision manufacturing processes, such as fine line etching and precise alignment, require advanced equipment and technology, which increases production costs.
Design complexity is also a key factor. The design and manufacture of flexible PCBs involve multiple processes, such as etching, copper plating, drilling, etc. The higher the complexity of the process, the higher the manufacturing cost.
Finally, market demand also affects the cost of flexible PCBs. Mass production can effectively reduce unit costs, while small batch or customized production may lead to higher costs.
What is rigid-flex PCB vs flex PCB?
The main difference between rigid-flex PCB and flexible PCB lies in their structure and application scenarios. Rigid-flex PCB combines the characteristics of rigid PCB and flexible PCB, while flexible PCB is made entirely of flexible materials.
Rigid-flex PCB is a circuit board that combines rigid board and flexible board, and is usually used in areas where both rigidity and flexibility are required. This type of circuit board uses flexible materials in specific areas and remains rigid in other areas to meet complex design requirements.
Flexible PCB is made entirely of flexible materials and is usually used in applications that require high flexibility and space saving. Flexible PCB uses flexible materials such as polyimide, allowing the circuit board to be easily bent and folded in a small space. This type of PCB is widely used in modern smart devices such as smartphones, tablets and wearable devices to achieve smaller size and more complex functions.
What is the difference between FR4 and flex PCB?
The main difference between FR4 and flexible PCB lies in their materials, structure and application scenarios. FR4 is a rigid PCB substrate, mainly composed of glass fiber and epoxy resin, with good electrical properties and mechanical strength, suitable for applications requiring high stability and reliability. Flexible PCBs are highly flexible and bendable, suitable for applications with limited space or frequent bending.
FR4 features and applications:
FR4 is currently the most common PCB substrate. FR4 has good electrical properties, with a dielectric constant between 4.5 and 4.8, suitable for medium and low frequency applications; in terms of thermal performance, its thermal expansion coefficient is about 14-17ppm/°C, and its heat resistance can reach 260°C; in terms of mechanical properties, FR4 has high bending strength and tensile strength, suitable for manufacturing processes such as drilling, etching, and copper plating.
Due to its stability and reliability, FR4 is often used in applications such as display screens and reverse cam screens that require high stability.
Flexible PCBs features and applications:
Flexible PCBs (FPCs) are mainly made of materials such as polyimide and are highly flexible and bendable. They are often used in applications with limited size or frequent bending.
The design of flexible PCB is relatively simple, but when rigidity needs to be increased for easy installation or assembly, reinforcement plates such as PI, FR-4 or steel sheets are used.
Due to the high flexibility of flexible PCBs, they are often used in devices that require frequent movement or deformation, such as touch sensors and automotive lighting systems.
As a new type of PCB in the electronics field, high-temperature resistant flexible PCBs have gradually become a popular choice in the electronics field with their excellent high-temperature resistance, bendability, foldability, light weight, stable electrical performance, and good mechanical properties. High-temperature resistant flexible PCBs play an important role in applications in high-temperature environments such as aerospace, automotive electronics, industrial control, and medical equipment.