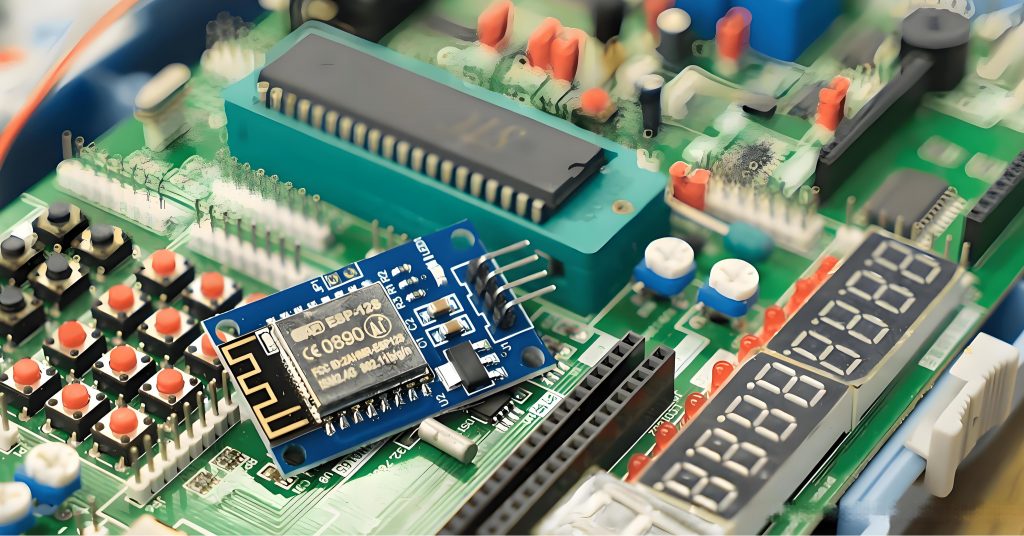
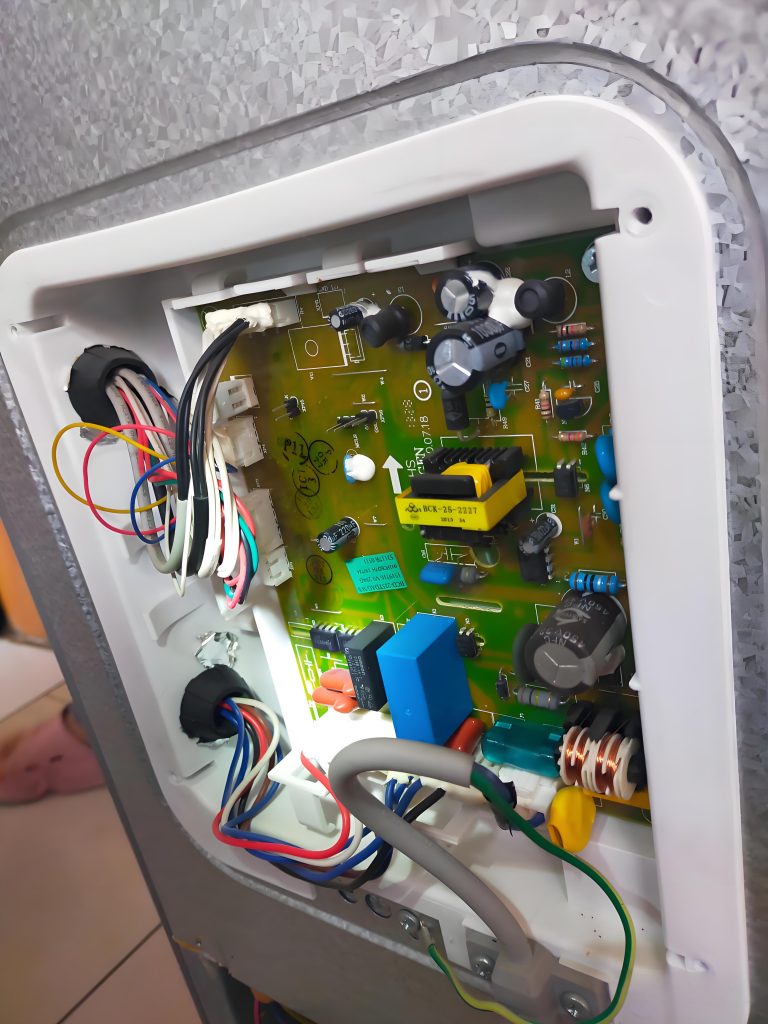
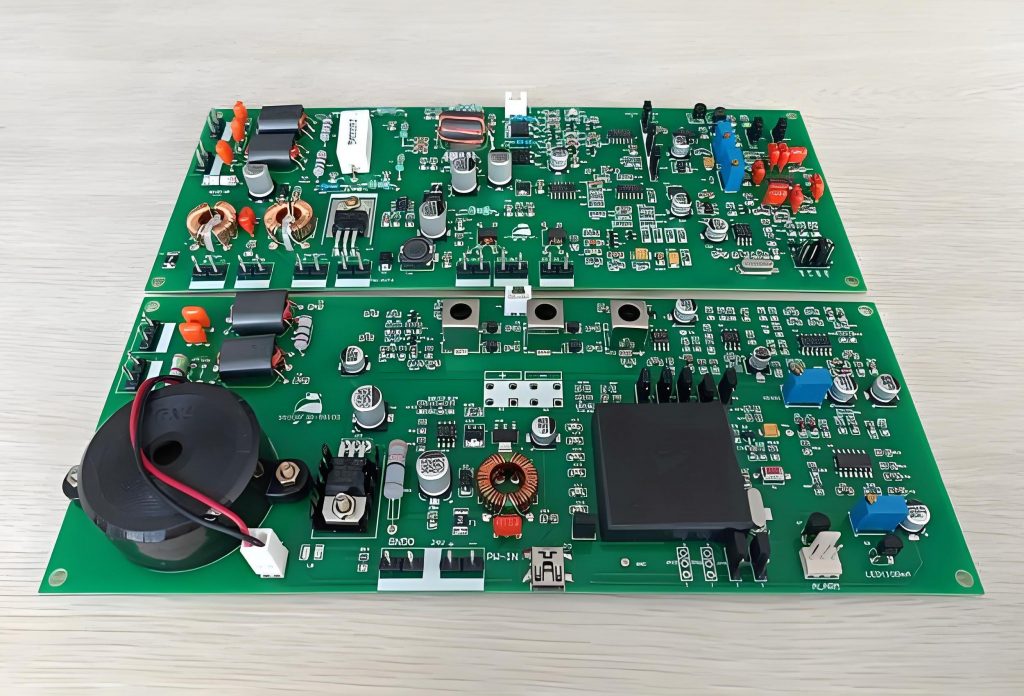
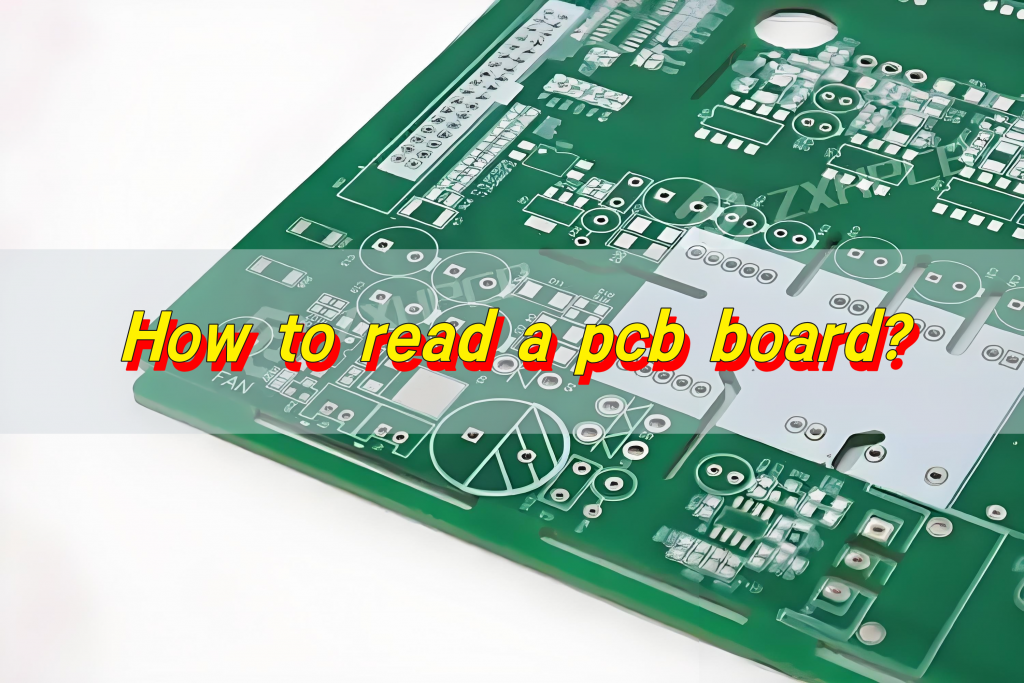
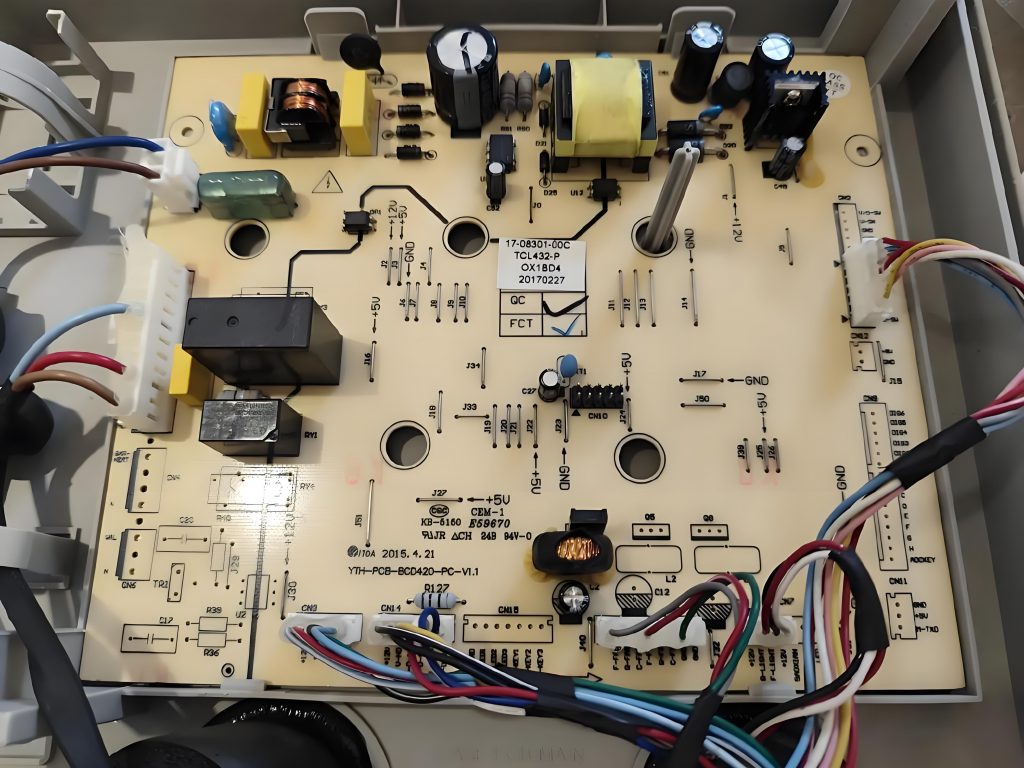
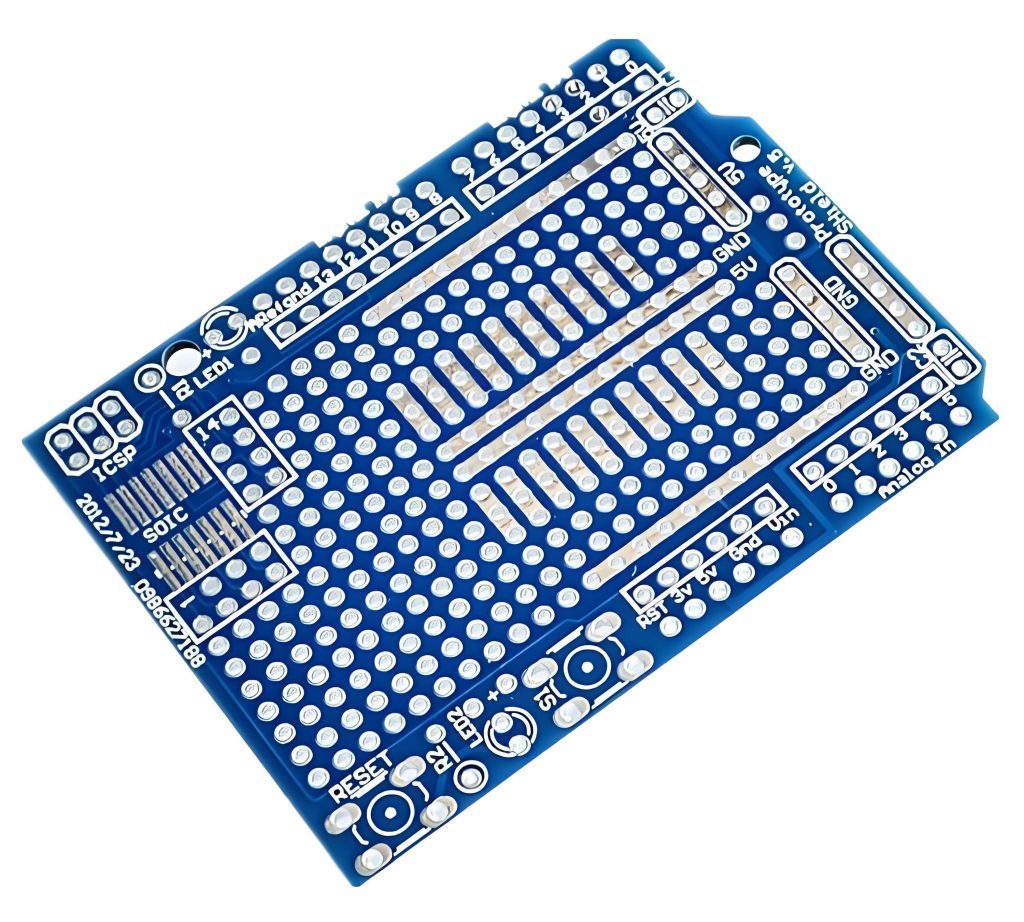
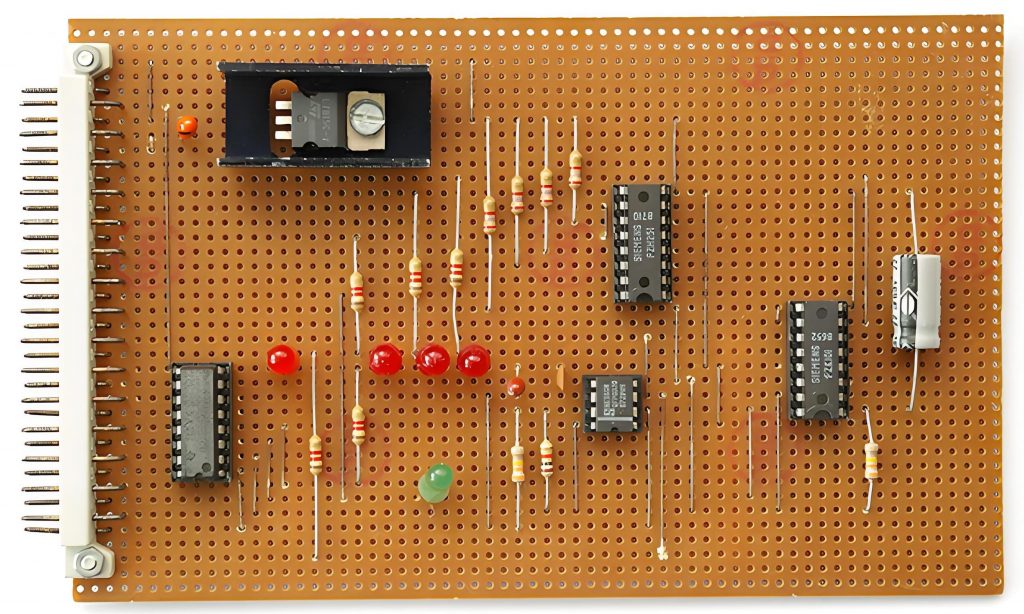
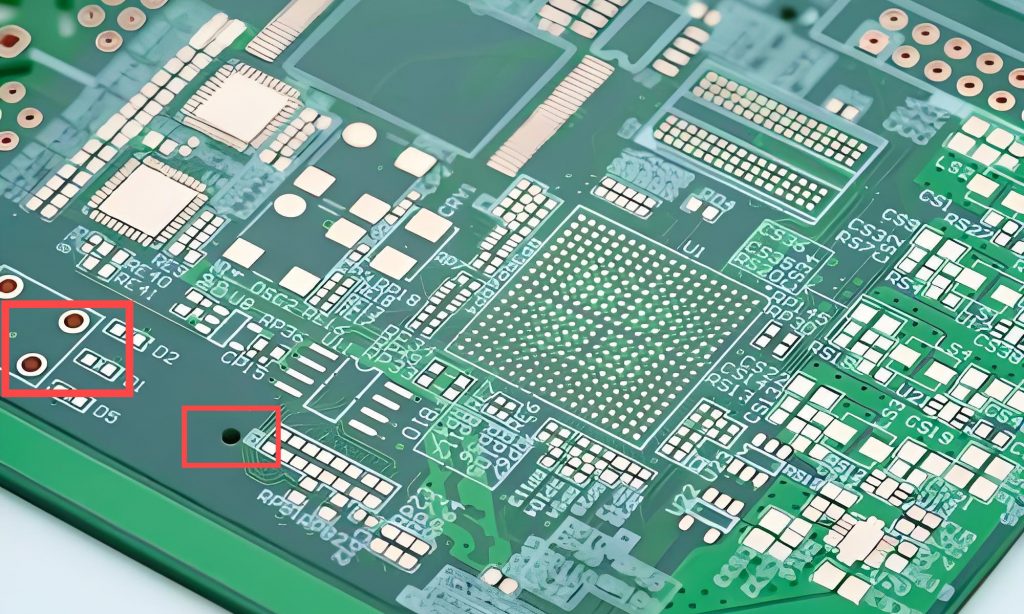
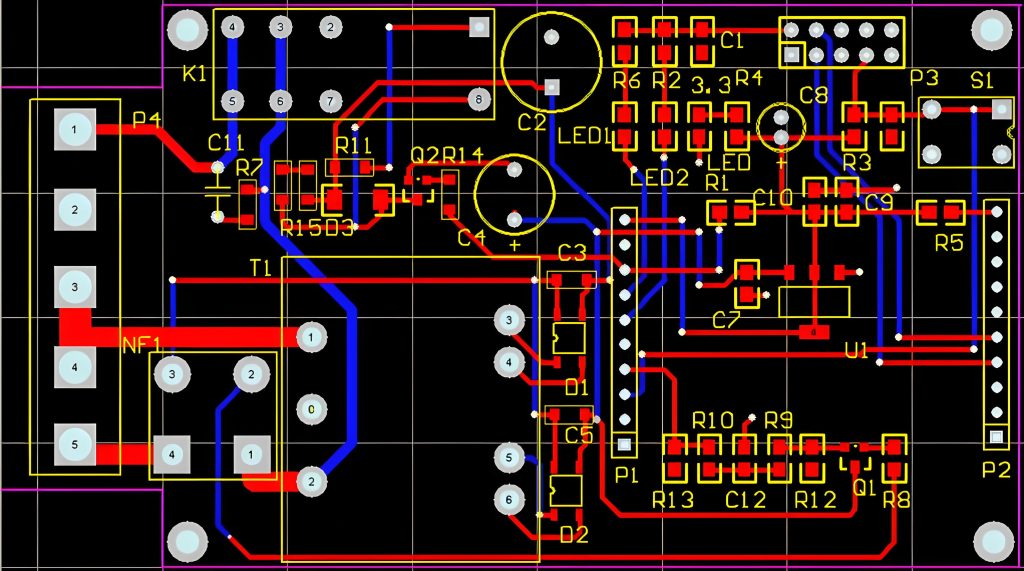
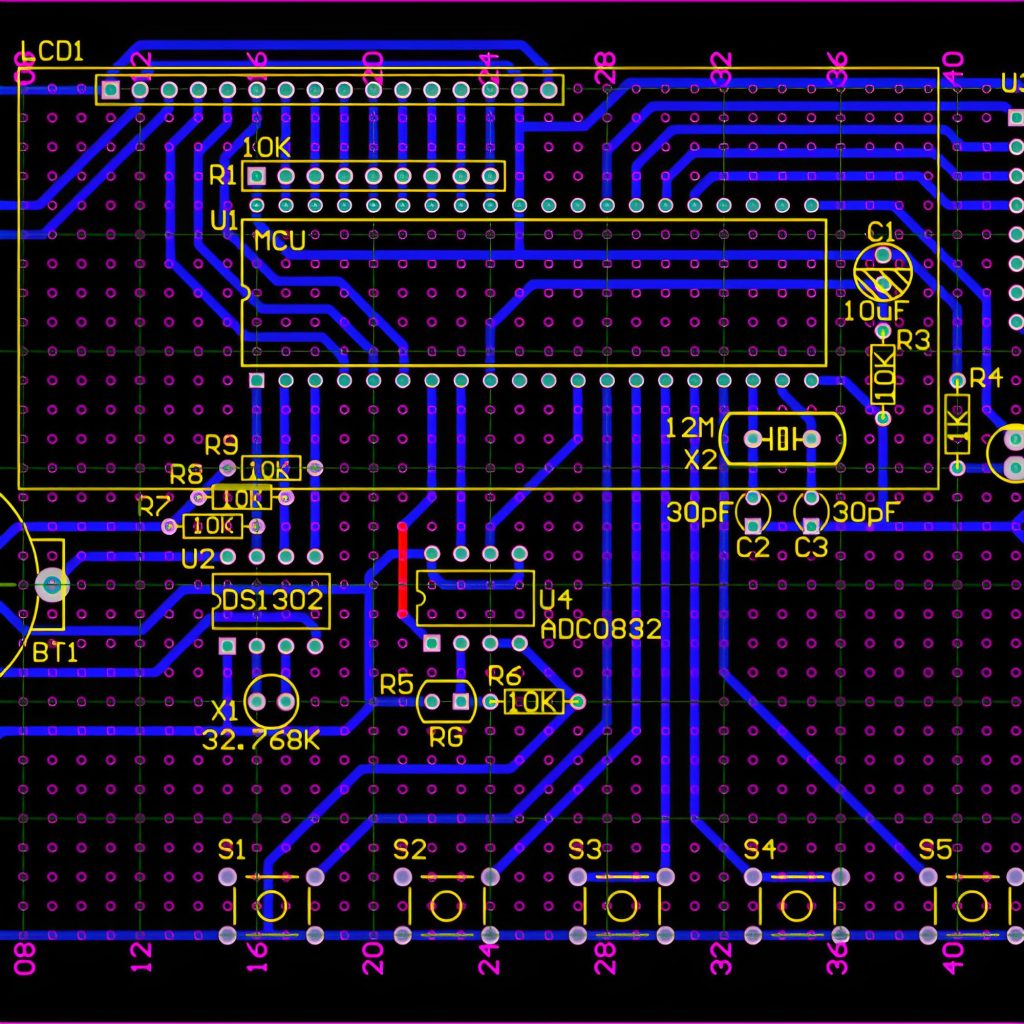
How to read a pcb board? When reading a PCB board, you need to pay attention to several aspects: First, the substrate, such as FR4, is green or brown, the ceramic substrate is white and brittle, and the aluminum substrate has a metallic texture, and their characteristics are different.
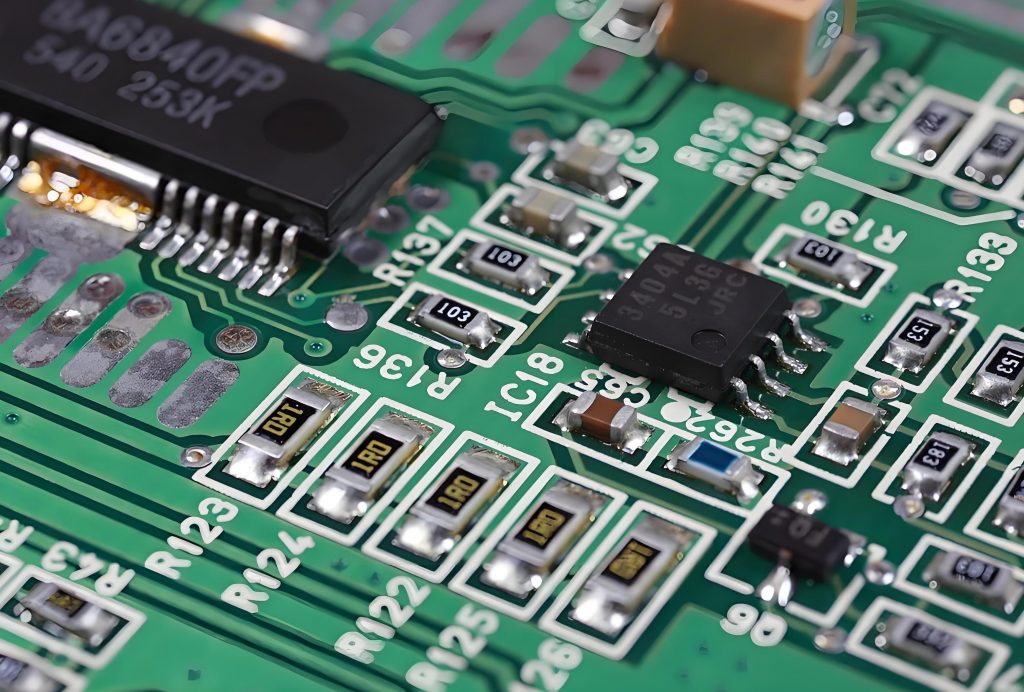
Second, identify the components. Resistors are mostly small cylinders with two pins, marked with resistance values, and play the role of current limiting and voltage dividing; capacitors have various shapes, electrolytic capacitors have polarity for filtering, and ceramic capacitors have no polarity for coupling; integrated circuits are multi-pin black chips, and their functions are known by model; transistors have three pins and can amplify or switch signals.
Finally, pay attention to solder joints, vias, test points and markings. The solder joints should be good, vias connect multi-layer lines, test points help detection, and markings help track circuits and understand component parameters and areas, so that you can understand the PCB board.
How to read PCB for beginners?
The steps and methods for beginners to read PCB are as follows:
- Observe the overall structure: First, carefully observe the overall structure of the circuit board, pay attention to the shape, size and color of the circuit board, as well as the markings and labels on it.
- Identify electronic components: Try to identify various electronic components on the circuit board, such as resistors, capacitors, inductors, diodes, transistors, integrated circuits, etc.
- Trace the circuit path: Trace the wire path on the circuit board and understand how the circuit is connected. Pay attention to the direction and connection of the wires, and try to trace the circuit path from one component to another and the connections between them.
- Analyze the circuit board hierarchy: A complex circuit board usually consists of multiple layers. By observing the structure and hierarchy of the circuit board, you can infer the function and design of the circuit board.
- Read the circuit board markings: There are usually markings, labels, printed text or icons on the circuit board to indicate components, connections or other important information.
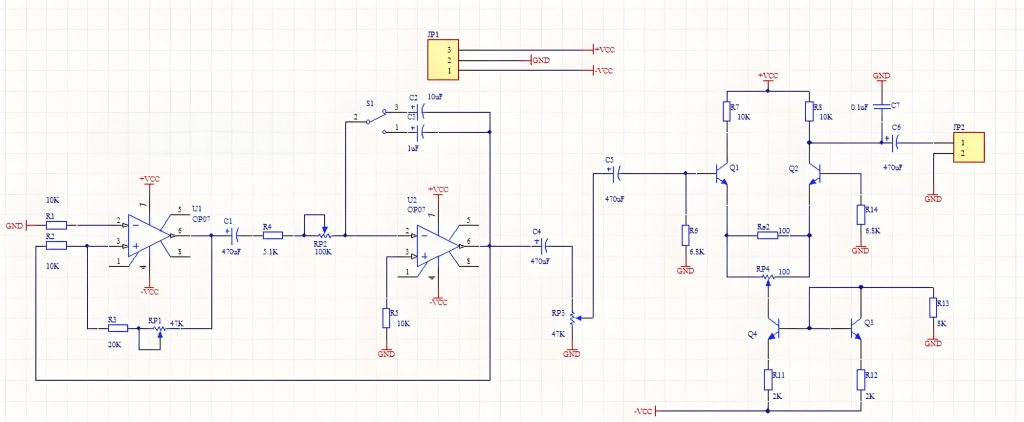
- Reference circuit diagrams and documents: Get the circuit diagram or related documents of the circuit board. The circuit diagram is a graphical representation of the circuit on the circuit board, which can provide more detailed information.
- Learn basic circuit knowledge: In order to better understand the circuit board, it is recommended to learn some basic circuit knowledge. Understand the basic concepts such as current, voltage, resistance, capacitance in the circuit, as well as common circuit topologies and circuit analysis methods.
How do you analyse a PCB board?
Analysis of PCB boards can be carried out from the following aspects:
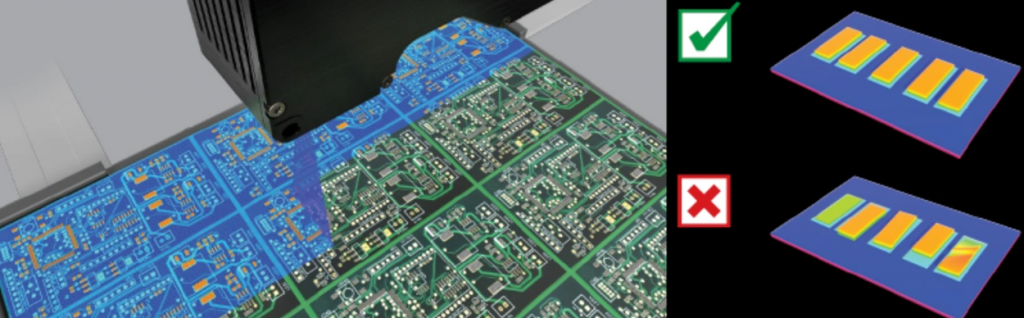
- Check the ink quality: high-quality PCB boards usually use well-known brands of ink, and the printing and baking process is exquisite. Excellent ink has better gloss and thickness.
- Observe the silk-screen text: the silk-screen text of high-quality PCB boards is clear and three-dimensional, and it is difficult to find the roughness of the edges of the handwriting even under a magnifying glass.
- Check the smoothness of the V-cut: high-quality PCB boards are more delicate in V-cut processing, and the edges are smooth and free of burrs.
- Evaluate the color of the board: the color of the board is uniform and there is no obvious color difference, indicating that the production process is stable and the quality is more guaranteed.
- Check the packaging material: high-quality packaging materials can usually better protect the PCB board and prevent damage during transportation.
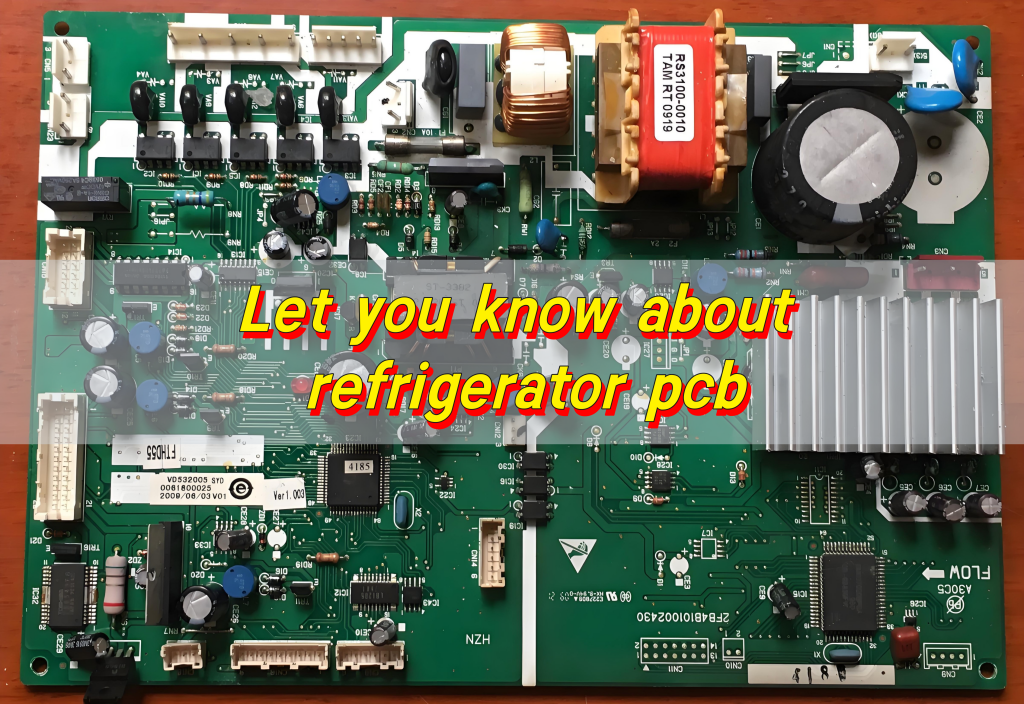
How do I identify parts of a PCB?
Identifying the various parts of a PCB (printed circuit board) requires understanding its basic structure and common components.
1. Basic structure
- Substrate: FR4 (mostly green or brown) is common, as well as ceramic and aluminum substrates. It mainly plays a supporting and insulating role.
- Copper foil circuit: observe the direction of the circuit, the thicker one carries large current, and the thinner one carries signals; multilayer boards should distinguish between the power layer and the signal layer.
2. Common components
- Resistors: small cylinders with two pins, you can see the markings to identify the resistance value. Used for current limiting and voltage division.
- Capacitors: various shapes, electrolytic capacitors have polarity, and ceramic capacitors have no polarity. Used for storing charge, filtering, etc.
- Integrated circuits (ICs): black rectangular chips, multiple pins, and model identification, which are the core of realizing complex functions.
- Transistors: bipolar and field effect types, three pins, used to amplify signals or as switches.
3. Others
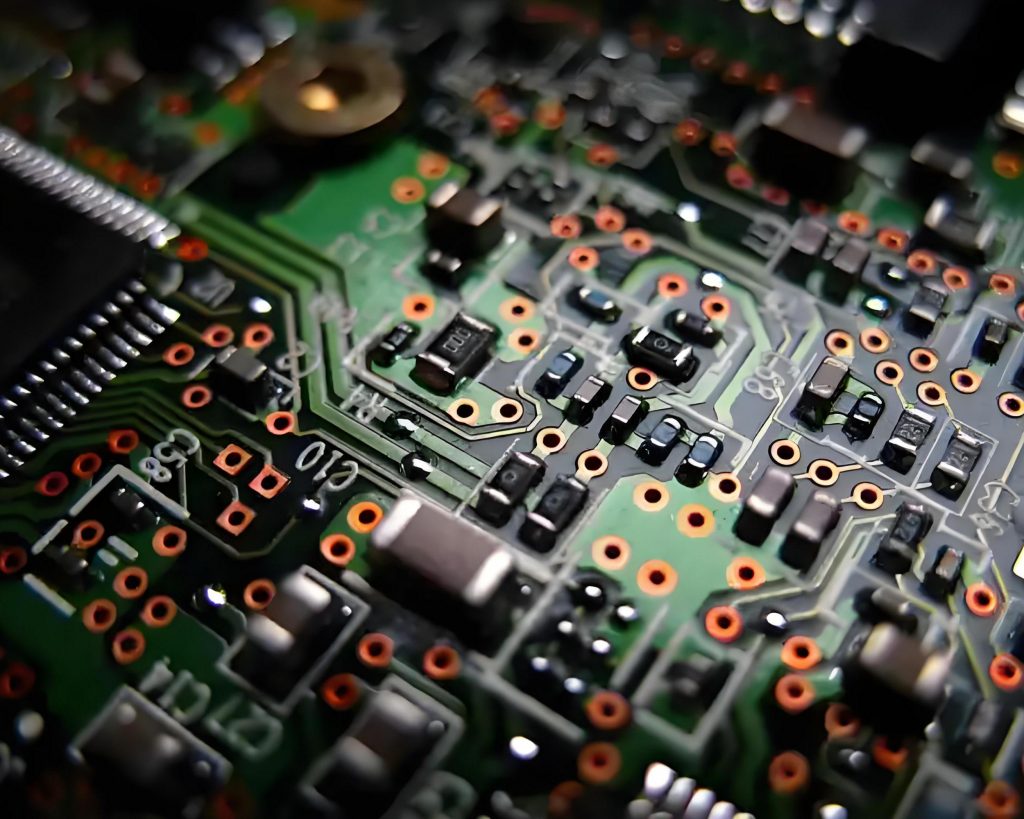
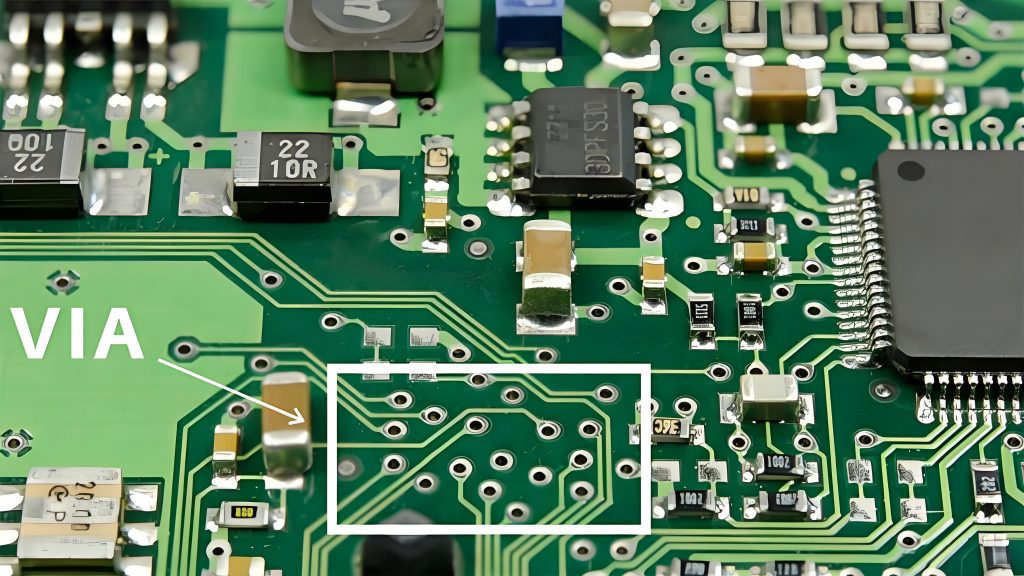
- Solder points and vias: Solder points connect components and circuits, and should be full and smooth; vias are used to connect different layers of circuits.
- Test points and logos: Test points are used for electrical testing, and logos contain information such as component numbers and values ââto help understand circuits.
How do you identify PCB material?
To identify PCB (printed circuit board) materials, you can start from the following aspects:
1. Observe the appearance
- Color: green or brown may be FR4; white and hard and brittle may be a ceramic substrate; silver with a metallic texture may be an aluminum substrate. Color sometimes also implies performance, such as black PCB may have a special design to resist electromagnetic interference.
- Texture and thickness: touch it with your hand, FR4 is harder and tougher, ceramic is hard and brittle, and aluminum substrate has a metallic texture. The thickness of PCBs for different devices is different, simple devices are thinner, and complex devices are thicker.
2. Reference environment and scenario
- High temperature environment: Ceramic or metal substrates may be used in high temperature environments, such as automobile engines and industrial furnace control circuits, and aluminum substrates are often used in electric vehicle motor controllers.
- High humidity environment: High humidity environment requires materials to be moisture-proof. FR4 has a certain moisture-proof ability. Some PCBs that have been specially treated or coated with moisture-proof paint can better resist moisture.
- High-frequency circuit application: The key to high-frequency circuits is dielectric constant and loss factor. For example, 5G communication equipment and radar systems may use special materials such as polytetrafluoroethylene boards, such as 5G base station antenna boards.
3. Check markings and documents
- PCB surface markings: Check whether there are manufacturer markings, material types, certification marks, etc. on the surface, such as UL and RoHS certification, to obtain material clues.
- Product documents and specifications: Find keywords such as “Board Material” in product manuals, technical documents or PCB specifications to determine the material.
How do you find the number of layers in a PCB?
To determine the number of layers of a circuit board (PCB), you can use the following methods to identify it:
- 1. Check the edge: Observe the edge of the PCB. If you can see multiple layers of copper foil or laminated boards, then this may be a multi-layer PCB. Each copper foil represents a separate PCB layer.
- 2. Number of holes: Multi-layer PCBs usually have more connection holes. Observe the solder holes on the surface and bottom of the PCB. If there are many holes arranged at intervals, it is likely a multi-layer PCB.
- 3. Solder mask color: Different layers of a multi-layer PCB are usually distinguished by solder mask of different colors. Check the surface of the PCB to see if there are areas of different colors, which may indicate differences between the layers.
- 4. Printed markings: PCB manufacturers usually mark the number of layers on the PCB. Check if there are printed markings or labels on the PCB, which may show the number of layers of the PCB.
- 5. Through the light source: If you have a light source, you can try to illuminate the PCB in a transparent way. Through the PCB, you may be able to see the layout of the internal layers, which can be used to infer the number of layers of the PCB.
What do the numbers on a PCB mean?
The numbers on the PCB board are usually used to identify the category, function number and serial number of electronic components on the circuit board. Specifically, the letter before the number indicates the category of the component, such as R for resistors, C for capacitors, D for diodes, etc.
The number after the number indicates the serial number or function number of the component on the circuit board. For example, R107 means that the serial number of the first resistor is 107, and C118 means that the serial number of the first capacitor is 11812.
In addition, the number can also represent the functional area or module of the circuit. For example, “1” may represent the motherboard circuit, “2” may represent the power supply circuit, etc., which are determined by the circuit designer.
In some cases, the combination of letters and numbers before the number can also represent specific functions or interfaces, such as SW for switch, LED for light-emitting diode, etc.
What does f stand for on a circuit board?
The “F” on the circuit board usually stands for fuse. In the circuit diagram, the single letter “F” usually represents lightning arrester, while the combination of letters has different meanings, such as “FU” for fuse and “FR” for thermal relay. This is a common representation method in electronic components.
To read the PCB board, you must first identify the substrate material, and then identify various electronic components, such as resistors, capacitors, integrated circuits, transistors, etc., understand their appearance characteristics and functional roles, so as to clarify the circuit connection and signal direction, and thus understand the circuit logic of the PCB board.