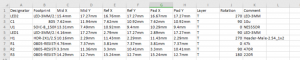
Even though we live in a world full of electronic gadgets, electronic devices are still shrouded in mystery. The working principle of electronic projects may seem very abstract, as the interior of these gadgets does not seem to have any visible mechanical parts. There are no moving parts such as gears or shafts on the printed circuit board, nor any significant visual changes.
The flow of electricity is invisible and can only be perceived by the effect it produces. Therefore, for those who want to dabble in the field of electronics making, making electronics as a hobby can seem like an extremely challenging task. It seems hard to imagine building something without fully understanding the principles behind it.
What does PCBA mean?
PCBA is the abbreviation of Printed Circuit Board Assembly, which refers to the process of welding, inserting, etc. of electronic components to the circuit board, and welding, inserting, etc. PCBA is an indispensable and important link in the manufacture of electronic products, which directly affects the performance stability and service life of electronic products.
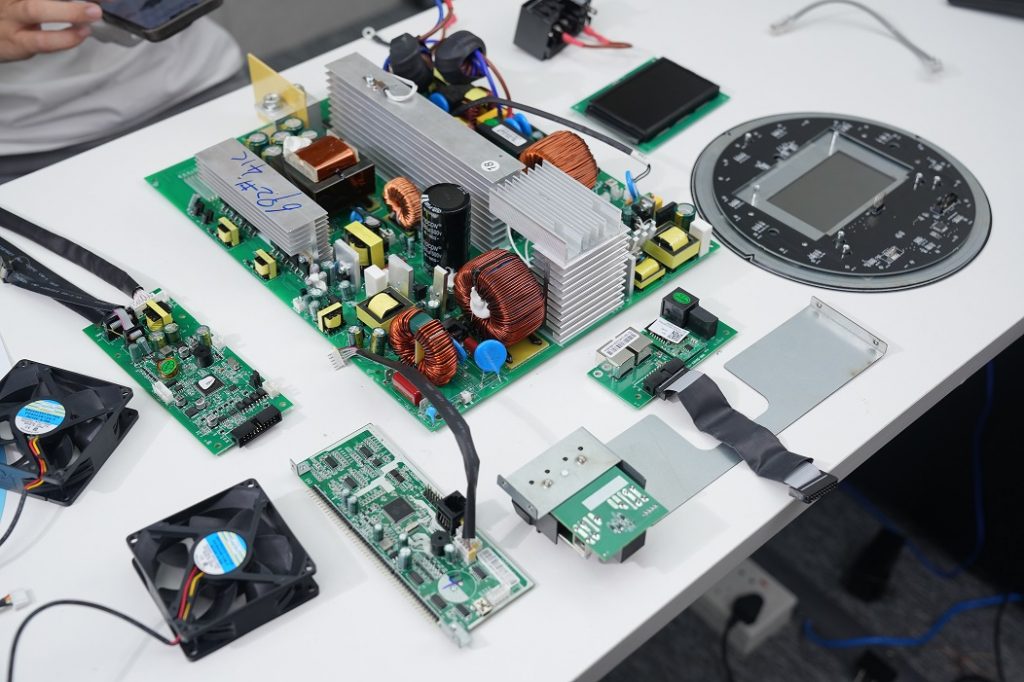

The manufacturing process of PCBA mainly includes components mounting, welding, post-welding processing and functional testing. The first is the component mounting, which is a process of welding the patch components, plug-in components, etc., to the PCB. Then there is welding, through traditional wave soldering or modern lead-free welding and other methods, the components are firmly fixed on the PCB. After that, the welding process is mainly to remove the welding slag on the PCBA surface, clean the PCBA surface, and check the solder joints and components of PCBA. Finally, the functional test is carried out, which is the last step in the PCBA process, and the PCBA is fully functional tested by various test equipment to ensure the stability and reliability of PCBA.
Applications of PCBA
PCBA products are widely used in various electronic products, such as household appliances, communication equipment, automotive electronics, industrial control equipment, etc. You can see it everywhere.
Different electronic products have different requirements for PCBA. Some require PCBA to be small and exquisite, some require PCBA to be high temperature and high pressure resistant, and some require PCBA to be waterproof and dustproof. With the rapid development of 5G, artificial intelligence, Internet of Things and other fields, PCBA will be more widely used, and PCBA’s performance and reliability requirements will also be higher.
Common components on a PCBA and their symbols
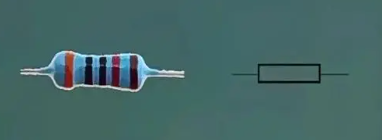
1. Resistor
Resistors are one of the most commonly used electronic components in PCBA, used to limit the current in the circuit. According to different materials, structures, and resistance values, resistors can be divided into fixed resistors, variable resistors, and special resistors. Resistors are widely used in various circuits, such as power circuits, amplification circuits, signal processing circuits, etc., to achieve current regulation and control.
2. Capacitor
A capacitor is a component that stores charge and electrical energy, with the characteristic of blocking direct current and passing alternating current. In PCBA, capacitors are commonly used in circuits such as filtering, coupling, tuning, and bypassing to improve circuit performance and stability. According to their different structures and applications, capacitors can be divided into fixed capacitors, variable capacitors, and fine tuned capacitors.

3. Inductor
Inductor, also known as induction coil, has the function of storing magnetic energy. In circuits, inductors can prevent changes in current and play a role in filtering and stabilizing the current. Inductance has a wide range of applications in power filtering, signal processing, and other fields.

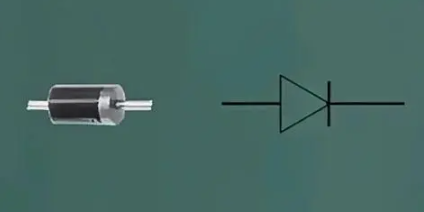
4. Diode
A diode is an electronic component with unidirectional conductivity, widely used in circuits such as rectification, detection, and voltage regulation. In PCBA, diodes can achieve functions such as voltage regulation, signal amplification, and switch control in the circuit. Common diodes include silicon diodes and germanium diodes, whose performance parameters such as forward voltage drop and reverse breakdown voltage determine their application scenarios.
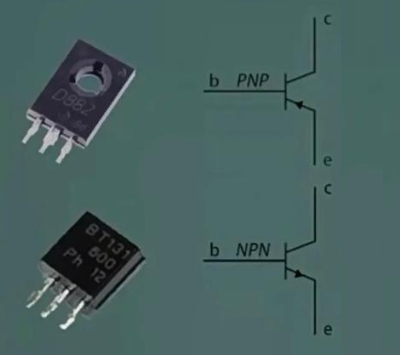
5. Transistor
Transistors are electronic components with functions such as amplification and switching, and are the core components that make up various circuits. In PCBA, transistors are commonly used in amplification circuits, oscillation circuits, switch circuits, etc. to achieve signal amplification, frequency conversion, and circuit control. There are many types of transistors, including bipolar transistors, field-effect transistors, etc., each with its own characteristics, widely used in various electronic devices.
6. IC Integrated circuit
Integrated circuit is an electronic component that integrates multiple electronic components on a single chip, with advantages such as small size, low power consumption, and stable performance. In PCBA, integrated circuits are key components for implementing various complex functions, such as digital signal processing, analog signal processing, communication interfaces, etc. Common integrated circuits include operational amplifiers, logic gate circuits, microprocessors, etc., which are widely used in various intelligent devices and systems.

7. Sensor
Sensors can sense physical quantities or states in the environment and convert them into electrical signals for output. In PCBA, sensors are commonly used to detect parameters such as temperature, humidity, light, pressure, etc., providing data support for intelligent control of electronic devices. There are various types of sensors with different performances, and choosing the appropriate sensor is crucial for improving the performance and user experience of electronic devices.

8. Controllable silicon rectifier (SCR)
Also known as thyristors, silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR) are similar to transistors and diodes – their working principle is essentially the coordinated operation of two transistors. Although SCR also has three pins, they are composed of four layers of silicon material instead of three layers, and are only used as switches, not amplifiers. Unlike single transistors that require continuous current to remain on, SCR only requires one pulse to activate the switch. They are very suitable for converting large amounts of electricity.
9. Crystal oscillator
Crystal oscillators provide clock signals in many circuits that require precise and stable timing. By physically oscillating piezoelectric materials (such as crystals), they generate periodic electronic signals, hence their name. Each crystal oscillator is designed to vibrate at a specific frequency, which is more stable, economical, and smaller in size than other timing methods. That’s why they are commonly used for precise timing in microcontrollers, or more commonly as clock components in quartz watches.

10. Switches and relays
A basic and easily overlooked component, a switch is simply a power button that controls the current in a circuit by switching between open or closed circuits. They vary greatly in appearance, from sliders, rotations, buttons, levers, toggles, key switches, and more. Similarly, a relay is an electromagnetic switch that operates through a solenoid, acting like a temporary magnet when a current flows through it. They act as switches and amplify small currents into larger ones.

Now that youâre familiar with some basic electronic components, why not dive into creating your own electronics project? Instead of starting with a complex project featuring advanced functions, begin with a few simple ones. As with any hobby, youâll encounter challenges along the way, but these hurdles are not insurmountable. With accessible and affordable beginner electronics tools like Arduino and CAD tools, the maker community welcomes new PCB designs and projects every day.
In addition to PCB manufacturing, Best Technology offers a full turnkey service, including parts procurement and assembly. Whether youâre working on prototypes or scaling up to mass production, Best Team provides a one-stop solution for seamless and hassle-free PCB assembly.