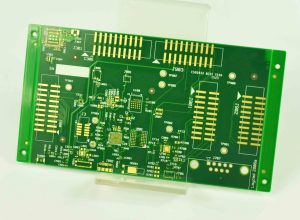
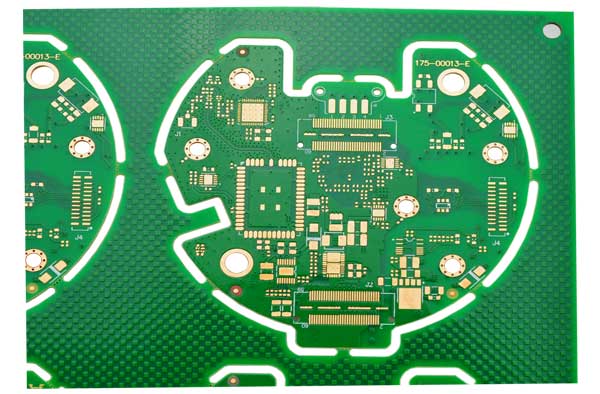
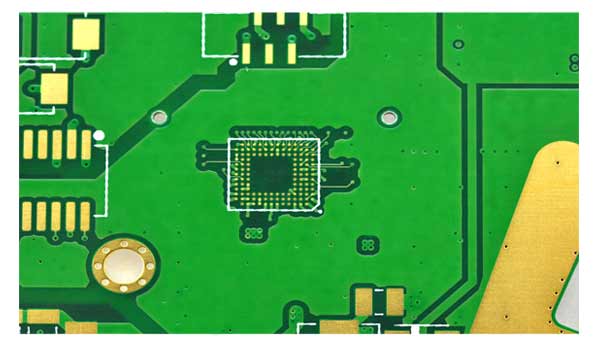
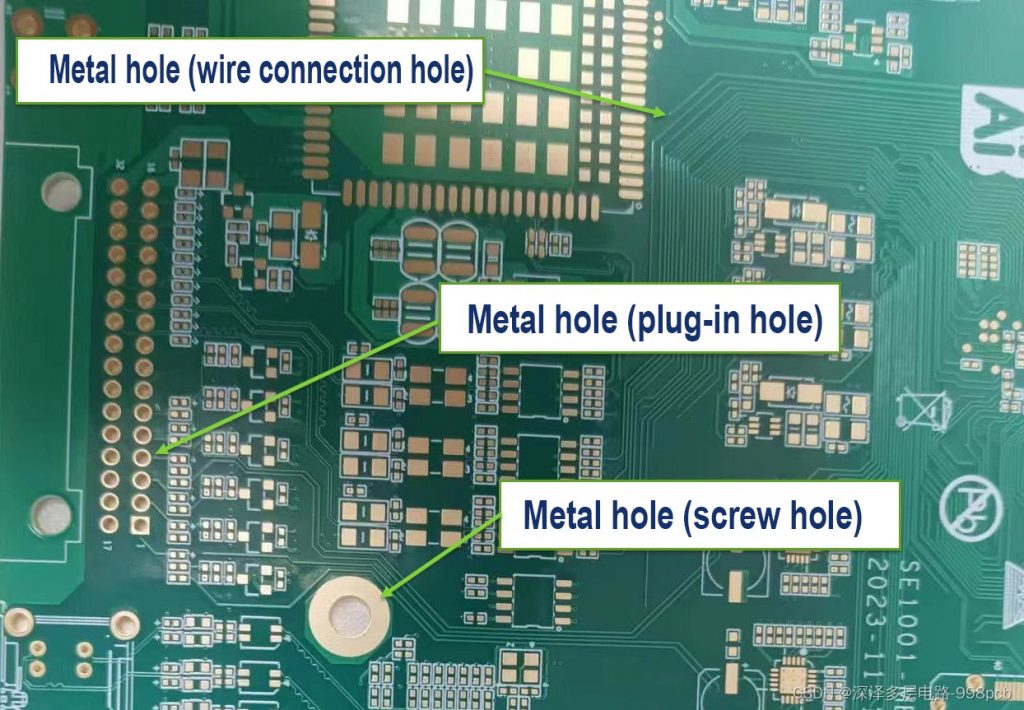
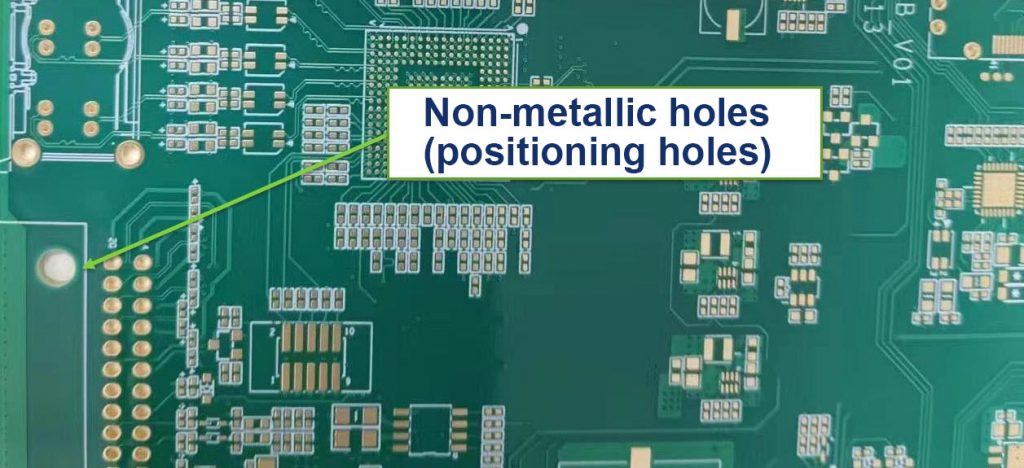
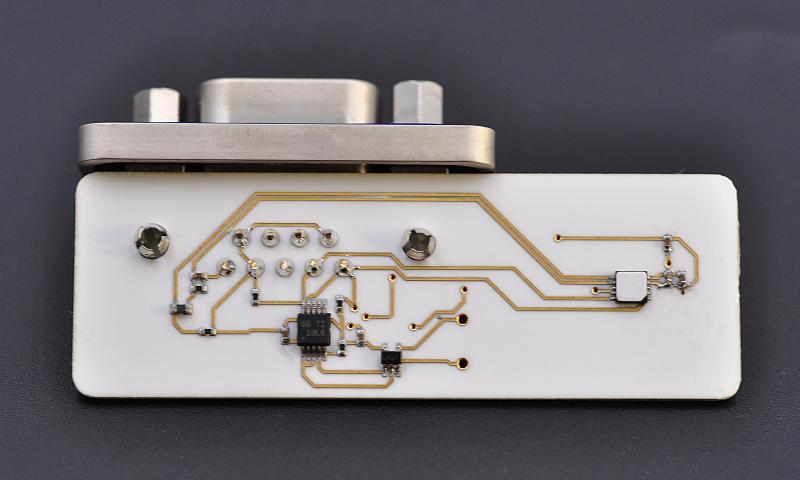
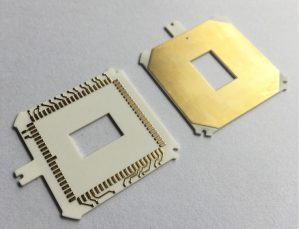
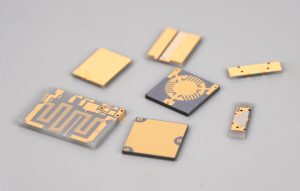
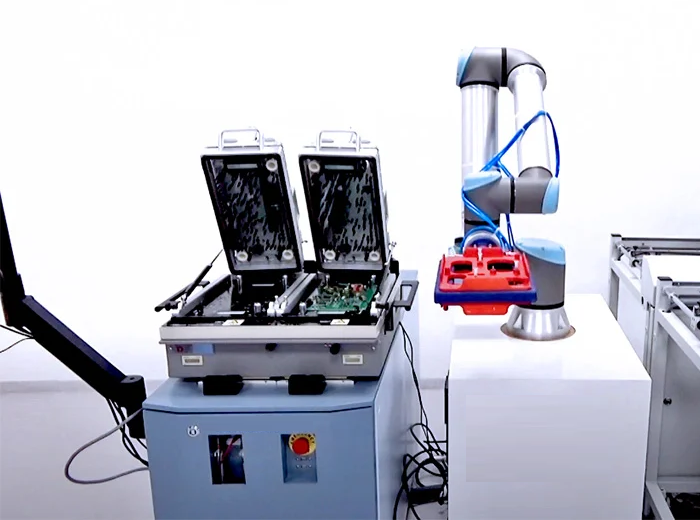
What is Aerospace PCB Assembly?
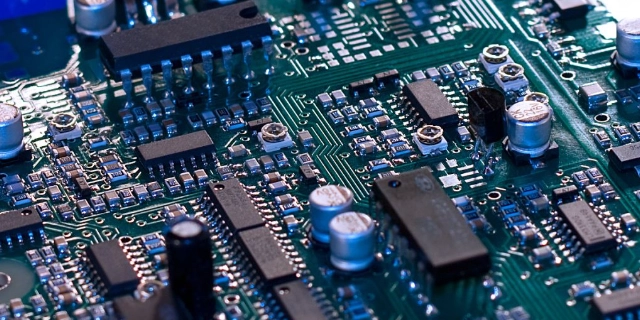
Aerospace PCB assembly refers to the intricate process of manufacturing printed circuit boards (PCBs) specifically for aerospace systems, including aircraft, spacecraft, satellites, and other related avionics systems. These boards are vital for controlling critical systems in extreme environments, where traditional electronic components would fail. Aerospace PCBs are engineered with precise attention to durability, signal integrity, and longevity to ensure reliable operation over long periods, even in the most hostile conditions like extreme temperatures, vibrations, and radiation.
The assembly process includes component placement, soldering, testing, and verification to ensure the PCBs meet strict aerospace industry standards. Due to the high-stakes nature of aerospace applications, each PCB must be built with the highest degree of precision and undergo rigorous testing to ensure it can withstand the operational conditions of the specific aerospace application.

Why does Aerospace PCB Assembly Need High Reliability?
Aerospace PCB assembly requires exceptionally high reliability due to the mission-critical nature of the systems they support. Unlike consumer electronics, where failures might lead to inconvenience, failures in aerospace systems can be catastrophic, leading to loss of life, property, or the failure of multimillion-dollar space missions. Once a satellite, spacecraft, or aircraft is deployed, accessibility to repair faulty components is extremely limited. So that aerospace PCBs function flawlessly for years, or even decades, without failure.
In addition to inaccessibility, aerospace electronics face harsh environmental conditions such as extreme temperatures, radiation, shock, and vibration. These conditions demand that PCBs operate continuously under stress without compromising their performance. High-reliability standards ensure the PCBs’ long-term stability and functionality in these demanding environments. Aerospace components must be high quality, fail-safe, and undergo extensive testing for performance, durability, and resilience.
What Grade of IPC Standard Should Aerospace PCB Assembly Follow?
IPC standards are a widely used term in the electronics industry that covers all aspects of electronic product design, including the acceptability of printed circuit boards, material requirements, and more. IPC standards establish standards from all aspects, as long as manufacturers strictly implement the standards, product quality and reliability are naturally guaranteed.
Aerospace PCB assembly needs to meet the requirements of high reliability, high quality and high performance, so during the production process, it should comply with IPC-6012 Level 3 standards. IPC-6012 is a performance specification document that defines the default requirements and specifications for each class of PCB. Among them, Class 3 PCBs have tighter tolerances and are commonly used in military applications, medical devices, and the aerospace industry. The IPC-6012 Level 3 standard ensures that the PCB can also ensure the reliable start-up and operation of the equipment in harsh environments, such as high temperature, low temperature, vibration and other extreme conditions can still work.
In addition to IPC-6012, IPC-610 Class 3 is critical for ensuring the highest quality workmanship in aerospace electronics as well. In the IPC-610 standard, class 3 defines the acceptance criteria for high-reliability electronics, including tight tolerances, high-quality soldering, and thorough inspections.
Industry Standards for Aerospace PCB Manufacturing
Aerospace PCB manufacturing must adhere to several industry-specific standards to ensure reliability and safety.
- ISO9001
It is an internationally recognized quality management system standards designed to help organizations continue to provide products or services that meet customer and applicable legal and regulatory requirements through a systematic approach. It is the code of conduct that governs our production process.
- AS9100
Another essential standard is AS9100, which is a widely recognized quality management system tailored specifically for the aerospace industry. It covers every aspect of the aerospace PCB production process, from material selection to assembly, testing, and delivery.
- MIL-PRF-31032
It is one of the most significant standards is MIL-PRF-31032, which governs the qualification of printed wiring boards used in military and aerospace applications.
- RoHS
PCBs for aerospace applications must also comply with RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) regulations, particularly in Europe, to ensure the environmental safety of electronic components. Additionally, aerospace PCBs undergo specific testing procedures, such as thermal cycling, vibration testing, and humidity resistance, to ensure they meet operational standards.
Best Technology certificated by ISO9001, ISO13485, IATF16949, AS9001, RoHS and some other certifications about manufacture. We are dedicated to provide customers with “High mixed, low volume, fast delivery and high quality” PCB and PCBA products. At Best Technology, you get a sense of value for money!
Common PCBA Modules or Systems for Aerospace Electronics
Aerospace electronics rely on various specialized PCBA modules and systems to ensure efficient and reliable operation in mission-critical environments. These systems are essential in everything from flight control to communication, navigation, and power management in aircraft, satellites, and spacecraft. Below are some of the most common PCBA modules or systems used in aerospace electronics:

1. Avionics Control Systems
Avionics control systems are the backbone of modern aerospace technology, responsible for managing and controlling various systems in aircraft and spacecraft. They handle critical functions such as navigation, communication, and onboard sensors, providing real-time data to pilots and flight computers.
2. Power Management Systems
Power management systems in aerospace electronics regulate the distribution and control of electrical power across the aircraft or spacecraft. These PCBA modules are designed to manage the onboard electrical grid. In some subsystems, they provide a stable power supply, such as for communication equipment, control systems, and sensors.
3. Flight Control Systems
Flight control systems are responsible for managing an aircraft‚Äôs or spacecraft’s attitude, direction, and speed. The PCBA modules within these systems process data from various sensors (like gyroscopes and accelerometers) and use it to adjust control surfaces or thrusters.
4. Radio Communication Systems
It enables the communication between the aircraft and ground control. RF (Radio Frequency) modules, transceivers, and antenna control units are common PCBAs in communication systems. Aerospace communication systems are engineered to handle long-distance transmission and are resistant to environmental interference, such as radiation or electromagnetic noise.
5. Navigation Systems
Navigation systems in aerospace electronics guide aircraft and spacecraft to their destinations using data from GPS satellites, inertial navigation systems (INS), and other sources. The PCBAs in navigation systems are responsible for processing this data and providing accurate location, speed, and altitude information.
6. Radar and Sensor Systems
They are the most important parts in the aerospace applications, like collision avoidance, terrain mapping, and weather monitoring. They can process large amounts of data quickly and reliably, often using digital signal processors and field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) to handle real-time processing.
7. Environmental Control Systems (ECS)
Environmental control systems are responsible for maintaining optimal cabin and equipment conditions within an aircraft or spacecraft. These systems monitor and regulate air pressure, temperature, and humidity. The PCBAs used in ECS modules often featuring sensors that track environmental parameters and control systems that adjust them accordingly.
8. Data Acquisition Systems
Data acquisition systems collect and process data from various subsystems and sensors in aerospace applications. These PCBA modules are integral in spacecraft, aircraft, and satellites, enabling real-time data monitoring, analysis, and recording. Data acquisition PCBAs are designed to interface with different sensors, process data quickly, and transmit it to central control systems for further analysis. These systems must be reliable and capable of operating in high-altitude or space environments where temperatures and radiation levels can be extreme.
9. Power Distribution Units (PDUs)
Power Distribution Units (PDUs) manage the flow of electrical power to various subsystems within an aircraft or spacecraft. The PCBAs in PDUs ensure that power is efficiently distributed to essential systems, and they often include built-in protections against power surges, overloads, and short circuits.
Best materials for Aerospace PCB Assembly
Aerospace PCB mainly used high reliability and high temperature materials. Common material types are the following:
- High temperature substrate
Because aerospace electronic equipment is often in a high temperature environment, it is necessary to use high temperature substrate, such as polyimide (PI) and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE).
- Refractory materials
The aerospace field has strict fire safety requirements, so it is necessary to use good flame
retardant materials, such as polystyrene (PS) and Australian flame retardant epoxy resin.
- Corrosion resistant materials
There are some corrosive substances in the aerospace environment, so it is necessary to use materials with good corrosion resistance, such as special polyamides and special coatings.
- High electrical performance materials
In aerospace applications, circuit boards are required to have good electrical properties, including high impedance, low dielectric constant and low dissipation characteristics, so materials such as high frequency glass fiber cloth (FR4), polyimide (PI) and polytetraoxyethylene (PTFE) are often used.
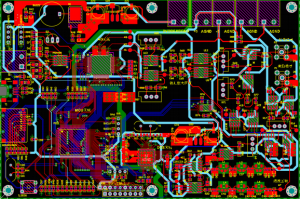
Aerospace PCB Assembly design standards
Designing PCBs for aerospace applications requires adherence to strict design standards that ensure optimal performance under harsh conditions. These design standards focus on several critical factors:
Signal Integrity
Aerospace PCBs must be designed to minimize signal degradation, ensuring accurate data transmission. High-speed signal transmission lines must be optimized for impedance control and reduced electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Thermal Management
Effective heat dissipation is crucial to prevent overheating in aerospace PCBs. The design must incorporate features such as metal cores or heat sinks to manage thermal loads efficiently.
Vibration and Shock Resistance
Aerospace PCBs are subject to extreme vibration and shock during flight or launch. The design must include mechanical reinforcements and vibration-dampening measures to protect the integrity of components and solder joints.
EMI Shielding
Aerospace environments are susceptible to electromagnetic interference, which can disrupt signal integrity. Proper shielding techniques, such as ground planes and shielded traces, are essential to reduce EMI and ensure reliable signal performance.
Component Placement
Components must be strategically placed to ensure signal integrity, reduce noise, and improve overall PCB performance.
Best Technology is a professional PCB & PCBA manufacturers in military, aerospace and medical, over 70% of our engineers have worked in PCB industry for more than 10 years. We have mature technology and advanced testing equipment to ensure the highest quality while maintain fast delivery. Trust us, we can be your most reliable PCB supplier in China and Vietnam.