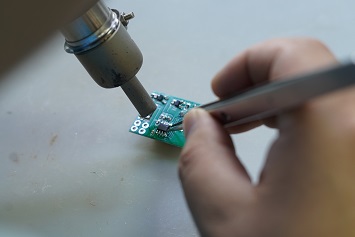
How to Use Soldering Paste? Soldering paste is a blend of tiny metal alloy particles and flux. It helps components bond to PCB pads during reflow. To use it, apply a small, even amount of paste to clean pads, place the component on top, and heat the area with a reflow oven or hot-air tool.
What Is Soldering Paste?
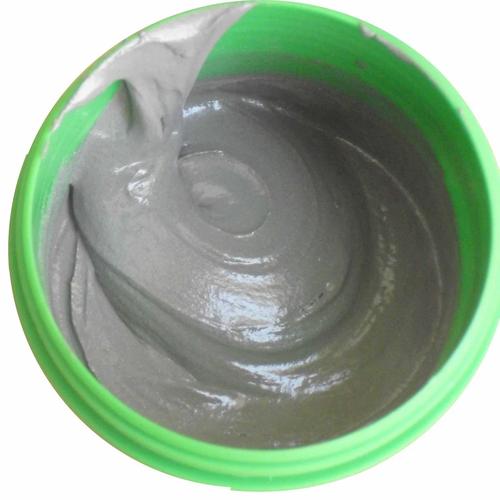
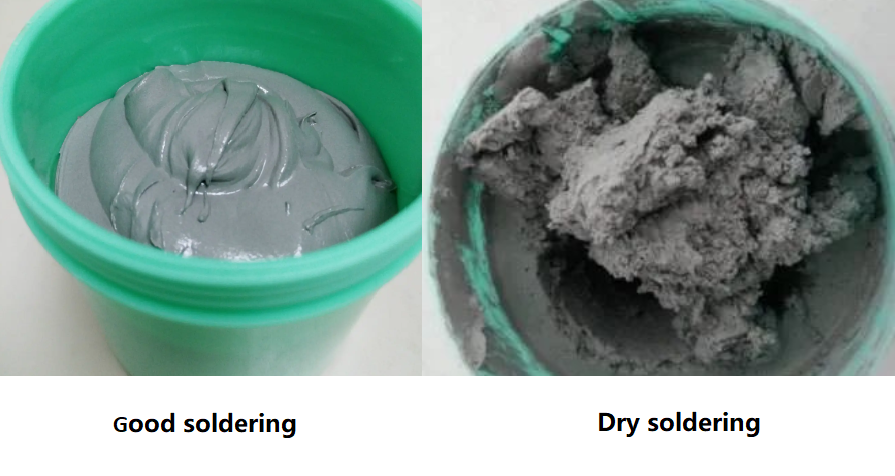
Soldering paste, also called solder paste, is a mixture that includes tiny metal alloy particles combined with a flux medium. It is soft, grey, and sticky. Engineers apply it to copper pads before placing components. After heating, the alloy melts, forms a bond, and creates electrical continuity.
In SMT production, solder paste acts like glue before reflow and becomes a strong metallic joint afterward. The paste stays in place during part placement. It wets surfaces when heated. It also removes mild oxidation.
You will see different types of solder pastes across the industry. Most of them follow either Sn-Pb or lead-free formulas. The choice depends on your process, compliance needs, and product application. Lead-free pastes dominate now since RoHS and other environmental rules require safer materials.
Types of Flux in Soldering
Flux is the active agent inside solder paste. Its job is simple but critical. It removes light oxidation, keeps surfaces clean, and helps molten solder spread.
There are several flux varieties. Each type serves a different function, depending on the complexity of your assembly, the metal surfaces involved, and the heating method.
1. Rosin Flux
Rosin flux comes from natural pine resin. It is stable, safe, and effective for a wide range of soldering tasks.
Rosin flux is available in different activity levels:
- R (low activity)
- RMA (medium activity)
- RA (high activity)
RMA is the most common. It strikes a balance between cleaning strength and low residue.
2. Water-Soluble Flux
Water-soluble flux uses organic acids and delivers stronger cleaning power. It is great for high-density circuits, oxidized surfaces, and complex PCBs.
Because residues are more active, water cleaning after reflow is required. This is one reason why it is popular in medical and industrial equipment production, where cleanliness is essential.
3. No-Clean Flux
No-clean flux leaves very small residues. These residues are safe, non-conductive, and do not need washing in most cases.
This flux is ideal for high-volume production where cleaning would increase cost. No-clean formulas save time, lower expense, and improve throughput.
4. Halogen-Free Flux
Halogen-free flux removes halogen compounds that can release corrosive by-products. This flux is widely used in green electronics, LED circuits, and consumer devices. It is stable and safe for long-term applications.
What Is Soldering Flux Made Of?
Flux ingredients vary depending on the type, but most formulas include these key components:
- 1. Activators
Activators break down surface oxides. They are mild acids or chemical compounds. Their strength determines how much cleaning power the flux offers.
- 2. Resins or Carriers
Resins form the base of rosin and no-clean flux. They provide viscosity and help residues stay stable.
- 3. Solvents
Solvents keep the paste flexible during printing and help it spread properly. They evaporate at high temperatures.
- 4. Additives
Additives control wetting, adhesion, viscosity, and residue color. They fine-tune performance for different use cases.
When everything works together, the flux streamlines the soldering process. It keeps the joint clean during heating, promotes good wetting, and improves overall reliability.
What Do You Do With Soldering Paste?
Solder paste has one main purpose: to bond components to PCB pads. But it offers other functions too. You can use solder paste for:
- SMT soldering
- Small electronic repairs
- Replacing QFN, BGA, or fine-pitch ICs
- Reflow soldering
- Hot-air soldering
- Tin filling on small pads
- Creating small metallic joins on test boards
It is not only a bonding material. It also ensures proper alignment and contact. Component placement machines rely on the adhesive quality of paste to hold parts steady before heating. This prevents movement and reduces defects.
Solder paste is essential in almost every production environment. It helps create strong, reliable joints used in phones, computers, robots, medical devices, and industrial systems.
How to Use Solder Paste Correctly?
Using solder paste correctly is essential if you want stable joints and good yields. The process is simple, but every step matters. Here is a clear, step-by-step guide.
Step 1. Prepare the Surface
Clean surfaces lead to strong solder joints. Wipe pads with isopropyl alcohol if needed. Remove grease, dust, oxidation, and fingerprints.
A clean pad helps the solder wet properly. Good wetting increases strength and lowers defect rates.
Step 2. Apply the Paste
There are two main ways to apply solder paste:
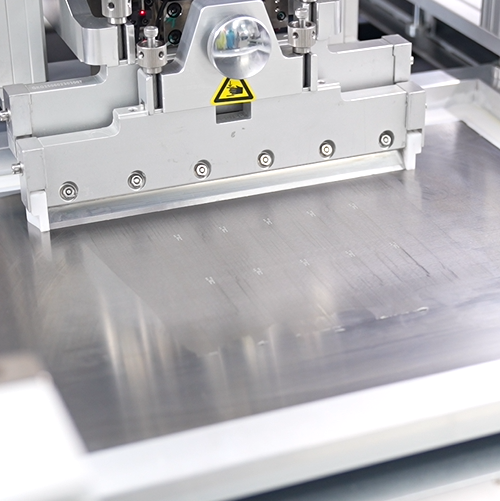
- Method A: Stencil Printing
Most SMT factories use stainless steel stencils. The stencil spreads paste on each pad with controlled thickness. The print is clean, uniform, and repeatable.
- Method B: Manual Application
For home repairs or prototypes, you can use a syringe. Push small dots of paste onto each pad. Keep the amount small and even. Too much paste can cause bridging.
Step 3. Place the Component
Place the component onto the pasted pads. The paste will hold it in place before heating. This tackiness prevents shifting. Manual tweezers or pick-and-place machines both work well.
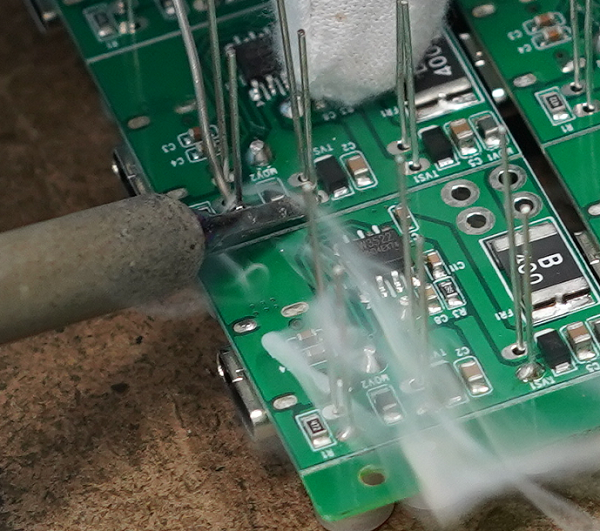
Step 4. Heat the Joint
Reflow the paste using:
- A reflow oven
- A hot-air gun
- A hot plate
- An SMT rework station
The heat melts the alloy. Flux activates. Oxides break down. Wetting occurs. The solder shrinks into a glossy, stable joint.
Make sure you follow the correct temperature curve. Good reflow depends on controlled heating.
Step 5. Let It Cool
Cooling should be even and smooth. After cooling, inspect the joint. A good solder joint looks shiny and well-formed.
Do I Need Flux for Solder Paste?
You do not need extra flux when using solder paste. That is because solder paste already includes flux in its formula. The flux inside the paste is optimized for wetting, cleaning, and bonding.
Adding more flux may help in rare special cases, but it is usually unnecessary. Too much external flux may leave extra residue or cause splattering during heating.
What Happens If You Donāt Use Flux When Soldering?
Flux is essential when soldering bare wire or loose solder. Without flux, oxidation will remain on the metal surface. The solder will not wet properly. The joint becomes weak and unreliable.
Here are the common outcomes when flux is missing:
- Poor wetting
- Weak joint strength
- Grainy or dull surface
- Increased bridging probability
- Higher defect ratio in production
- Risk of intermittent electrical contact
These issues make flux a must-use material for any reliable soldering process.
Can Solder Paste Be Used on All Metals?
Solder paste works well with common PCB metals, such as:
- Copper
- Tin
- Silver plating
- Gold plating
- ENIG finishes
- HASL finishes
- Immersion tin
- Immersion silver
However, it does not bond effectively with some metals, such as:
- Aluminum
- Stainless steel (without special flux)
- Nickel alloys (unless pre-treated)
- Oxidized surfaces
If your metal surface resists wetting, you may need a specialized flux or pre-treatment.
How Long Does Soldering Paste Last?
Solder paste does not last forever. Over time, solvents evaporate, flux loses activity, and metal particles oxidize. All these factors weaken printing quality and reduce wetting.
Most solder pastes last:
- Around 6 months refrigerated
- Around 1 month at room temperature
- Around 24 hours after opening, depending on humidity and airflow
To prolong lifespan, store it in a refrigerator around 2Ā°C to 10Ā°C. Warm it to room temperature before use. Do not open cold paste, or moisture will condense inside.
Common Problems When Using Solder Paste
Here are some issues that users may face, and what causes them.
- 1. Bridging
Too much paste or misaligned stencils create solder bridges.
- 2. Voids
Improper reflow or contaminated pads produce internal voids.
- 3. Tombstoning
Uneven heating or different pad sizes cause components to lift.
- 4. Incomplete Reflow
Low temperature prevents full melting.
- 5. Slumping
Low-quality paste spreads too much before heating.
All these issues are easy to prevent with good control and proper technique.
Conclusion:
Solder paste is a powerful material that makes modern electronics possible. It supports clean joints, stable conductivity, and quick assembly.
If you need help with SMT production, solder paste selection, or high-precision PCB assembly, Best Technology can support you with professional guidance and reliable manufacturing.
For inquiries, please contact: sales@bestpcbs.com