What is solder paste inspection? In simple terms, solder paste inspection is the process of inspecting and evaluating the quality, volume, shape, position and other parameters of solder paste printed on PCB. As the key material for connecting electronic components to PCB, the quality of solder paste printing directly determines the quality of soldering, which in turn affects the electrical and mechanical properties of PCBA.
How does solder paste inspection work?
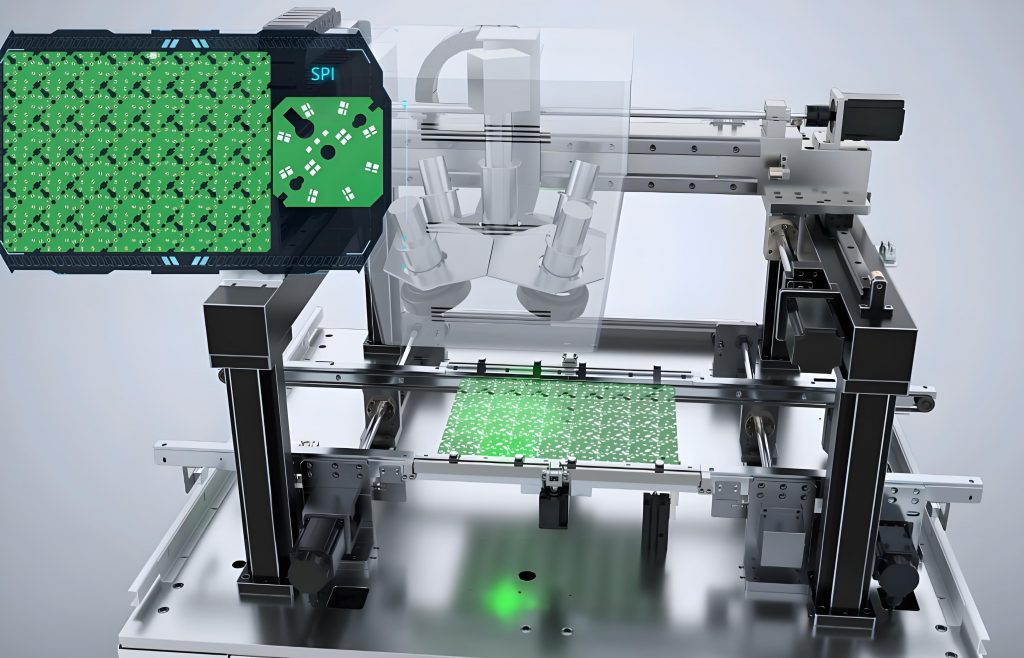
The working principle of SPI solder paste inspection equipment is mainly based on optical principles and laser triangulation technology. The equipment irradiates the soldering surface through a camera and a light source to obtain an image of the solder paste, and then detects and analyzes the shape, size, position, etc. of the solder paste through image processing technology to determine the quality of the solder paste and the welding effect.
Specifically, when the solder paste is scanned by a laser, the laser emits a laser, which is reflected and focused by the lens to irradiate the laser onto the solder paste. Due to the reflection of the solder paste, a part of the laser is reflected back and captured by the camera. By calculating the time difference between laser emission and reception, parameters such as the height and area of āāthe solder paste can be determined.
Specific steps and principles of SPI solder paste detection
- Image acquisition: Use a high-definition camera and light source to take pictures of the solder paste on the pad on the PCB surface to collect images.
- Image processing: Analyze and calculate the shape, size, position and other parameters of the solder paste through image processing algorithms, and compare them with previous standard data.
- Defect detection: Through comparative analysis, it is determined whether the printing has defects, such as solder paste offset, unevenness, less tin or more tin, etc.
Advantages of SPI solder paste detection
- Reduce the unqualified rate: The introduction of SPI can effectively reduce the unqualified rate of the original finished PCB by more than 85%, and significantly reduce the cost of rework and scrap by more than 90%.
- Improve the pass rate: Used in conjunction with AOI, through real-time feedback and optimization of the SMT patch proofing production line, the production quality can be more stable, and the unstable trial production stage that must be experienced when introducing new products can be greatly shortened.
- Make up for the shortcomings of traditional inspection: 3D inspection effectively makes up for the shortcomings of traditional inspection methods, especially for the inspection of micro components.
- Reduce bad situations: Through process control, minimize the bad situations of components after the furnace.
- Ensure printing quality: It can effectively ensure good solder paste printing quality and greatly reduce the possible defective rate of finished products.
What does solder paste inspection do?
Solder paste inspection has the following main functions:
- Ensure welding quality: The amount and shape of solder paste directly affect the welding effect. Through inspection, it can ensure that the amount of solder paste is moderate, avoid short circuits caused by too much solder paste, or problems such as cold soldering and open circuits caused by too little solder paste, thereby improving the reliability of solder joints and the electrical performance of products.
- Optimize the production process: Solder paste inspection can promptly detect problems in the solder paste printing process, such as printing position offset, tinning, etc. This helps to adjust and calibrate the printing equipment, make the printing process more accurate and stable, and improve production efficiency.
- Ensure product consistency: When mass-producing electronic products, solder paste inspection can ensure that the solder paste state on each circuit board is relatively consistent. This can keep the product’s soldering quality at a stable level, reduce product quality fluctuations, and improve the overall quality and consistency of the product.
How to measure solder paste height?
In SMT (surface mount technology), there are several main methods for measuring solder paste height:
- Laser scanning method: Using the principle of laser triangulation, the laser beam scans the solder paste surface and calculates the solder paste height by the angle change of the reflected light.
- Microscope method: By adjusting the focal length of the microscope, the focal plane coincides with the solder paste surface, and the height information at this time is measured using the optical system.
- Mechanical contact measurement method: Use a measuring instrument with a high-precision probe to contact the solder paste surface through the probe, and convert the displacement into an electrical signal to determine the solder paste height.
What does AOI mean in inspection?
AOI is automatic optical inspection, which uses cameras and optical components to obtain images of the PCB of the object being inspected, and then analyzes these images through image processing algorithms. These algorithms compare the actual image with the pre-set standard image or rules to identify various features on the surface of the object, such as the position, shape, size of the component, and whether the quality of the solder joint meets the requirements.
Principle and process of AOI detection
- Image acquisition: The AOI detection system collects image data on the surface of the product through a camera or sensor, including various details, components and connecting parts.
- Image processing: The received image data is processed by an image processing algorithm to remove interference, enhance image quality, and extract key information for subsequent analysis.
- Defect identification: Using pre-set models and rules, key features in the image are compared and analyzed to identify defects, misalignment or missing problems on the surface of the product.
- Alarm and classification: Once an abnormality is found, the AOI system will trigger an alarm mechanism and classify the defect type for subsequent processing and repair.
AOI detection systems are widely used in electronic manufacturing, printing industry and other fields. In electronic assembly production lines, it is used to detect PCB boards, solder joints, component positions, etc. to ensure product quality and reliability.
What is the difference between AOI and SPI?
AOI (Automated Optical Inspection) and SPI (Solder Paste Inspection) have the following main differences in SMT (Surface Mount Technology) processing:
1. Different inspection objects:
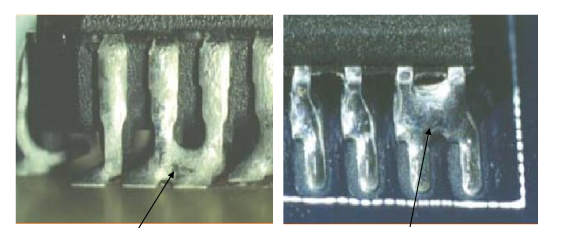
- AOI mainly inspects components and solder joints during SMT processing, and detects common errors such as component misalignment, reversal, missing, and redundant, as well as defects after soldering such as cold soldering and bridging.
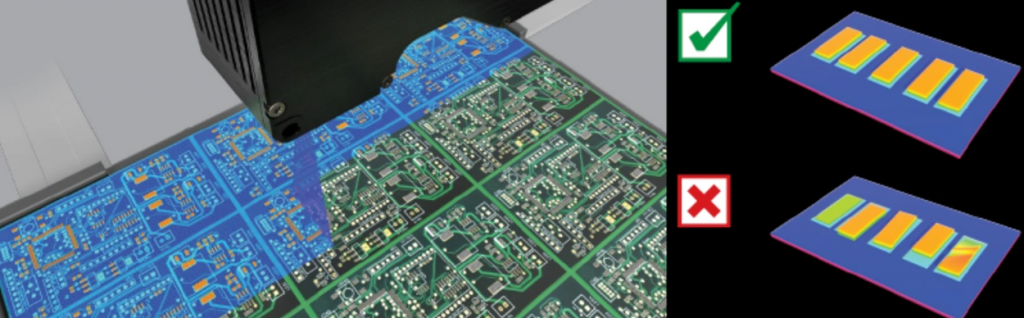
- SPI focuses on the quality assessment of solder paste printing. By measuring the volume, area, height and other parameters of solder paste, it evaluates the printing quality of solder paste and ensures the correct printing of solder paste.
2. Different inspection principles:
- AOI uses optical principles to analyze images on circuit boards and identifies defects through image processing algorithms. It uses a high-resolution camera to capture images of PCBAs and compares them with preset standard templates.
- SPI evaluates the printing quality of solder paste by measuring various parameters of solder paste, and uses 3D imaging technology to capture the three-dimensional shape of solder paste and compares it with standard data.
3. Different detection timing:
- AOI usually performs detection after component placement and welding. It can detect multiple welding points at one time after welding. The detection speed is fast and the impact on production efficiency is relatively small.
- SPI performs detection immediately after solder paste printing. Since it needs to be detected immediately after solder paste printing, it has a greater impact on production efficiency.
4. Application scenarios and advantages:
- AOI is suitable for high-demand SMT processing production lines. It can quickly and accurately detect a variety of defects and ensure the quality stability of circuit boards.
- SPI is crucial to ensure the quality of solder paste printing, directly affects the subsequent placement and welding effects of components, and is suitable for production lines that require high-precision solder paste printing.
What are the defects of SPI?
The defects of 3D SPI (Surface Inspection) mainly include the following aspects:
- Low laser resolution: The laser resolution of 3D SPI is generally at the level of 10-20um, which may not be ideal for precise circuit board detection.
- Repeatability accuracy is affected: Since each sampling can only provide information of one point, the repeatability accuracy of 3D SPI may be affected.
- Sensitive to external vibration: External vibration has a great impact on the detection effect of 3D SPI, and additional stabilization measures may be required to ensure the accuracy of the detection.
- Light conditions: The equipment relies on the principle of optical imaging for detection, so it has high requirements for the light conditions of the detection environment and needs to work under stable and uniform lighting conditions to ensure image quality and detection accuracy.
- Relatively slow speed: Compared with some other detection technologies, 3D SPI may be slower.
How long can solder paste sit before reflow?
Before the reflow process, the solder paste needs to stay for a period of time to adapt to the environment and ensure the reliability and quality of the solder joints. The optimal dwell time is affected by various factors, such as the freshness of the solder paste, recycled solder paste, ambient temperature and humidity.
The length of the dwell time directly affects the viscosity and fluidity of the solder paste, thereby determining the solder joint morphology and reliability. If the dwell time is too short, there may be gaps and cracks in the solder joint, which affects its reliability. If the dwell time is too long, the surface tension of the solder joint will increase, resulting in irregular morphology on the solder joint surface, which affects the power-on performance of the circuit.
In general, the best dwell time is between 4 and 8 hours. It should be noted that too long or too short a dwell time will affect the solder joint morphology and reliability. Therefore, in specific applications, it is necessary to select the best solder paste dwell time according to actual conditions.
In short, solder paste detection, as a key link in PCBA production, plays a vital role in ensuring the quality and performance of electronic products. Its detection methods cover visual inspection, 2D detection, and advanced 3D detection, each with its own advantages and disadvantages and applicable scenarios, and is a key line of defense to ensure the quality and performance of electronic products.