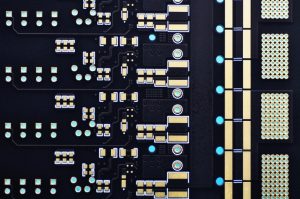
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the backbone of modern electronics. To ensure optimal performance and durability, PCBs undergo various surface treatments. These treatments protect the copper traces from corrosion, enhance solderability, and improve the overall reliability of the circuit board. In this article, we’ll explore the most common PCB surface treatments and their applications.
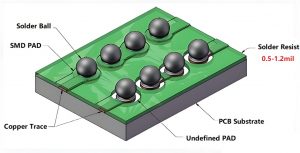
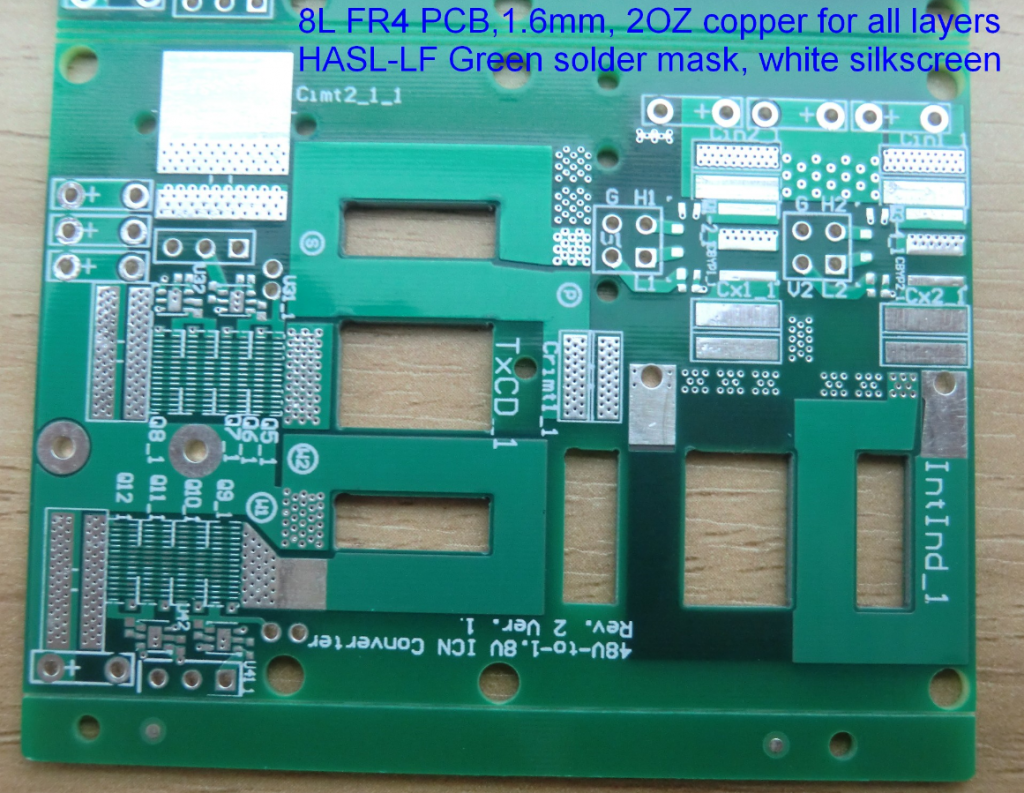
1. HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling)
Principle
HASL is a traditional surface treatment that involves immersing the PCB in a bath of molten solder. After the solder solidifies, hot air is used to level the surface and remove excess solder.
Features
â¢Material: Lead-tin alloy (for traditional HASL) or lead-free solder (for LF HASL).
â¢Process: Immersion in molten solder followed by hot air leveling.
Advantages
â¢Excellent solderability.
â¢Cost-effective for large volumes.
â¢Good mechanical strength.
Picture
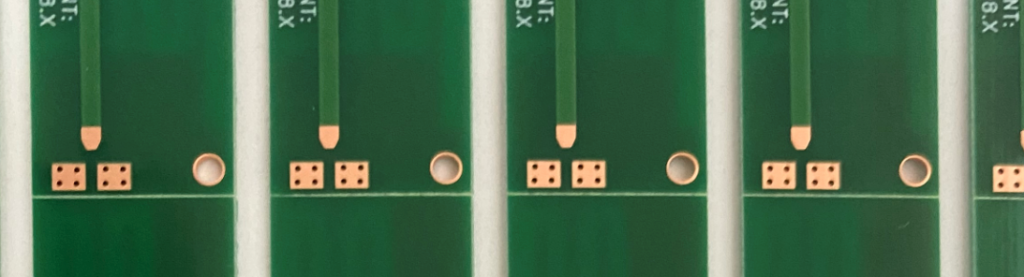
2. OSP (Organic Solderability Preservatives)
Principle
OSP involves applying a thin layer of organic material (usually a rosin-based compound) to the copper surface, which protects it from oxidation.
Features
â¢Material: Organic preservatives.
â¢Process: Application of organic film.
Advantages
â¢Environmentally friendly.
â¢Good solderability.
â¢Suitable for rework.
Picture
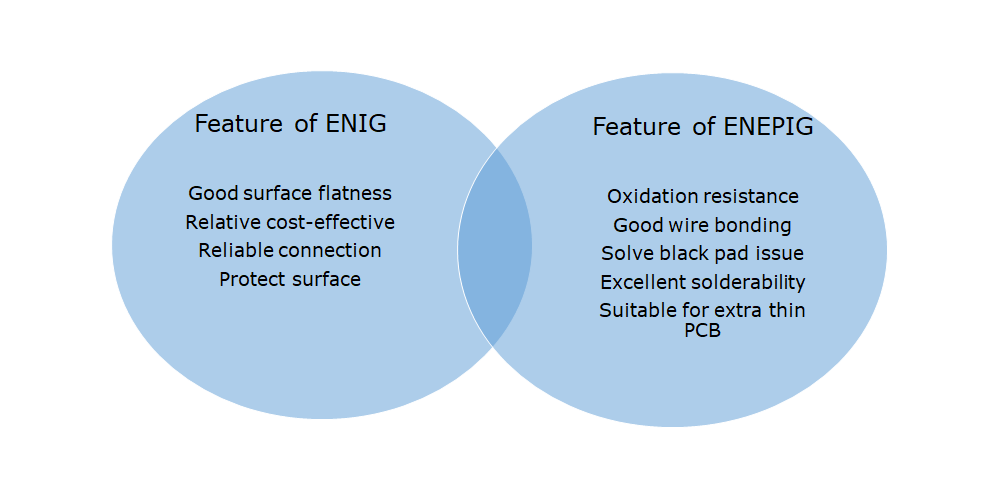
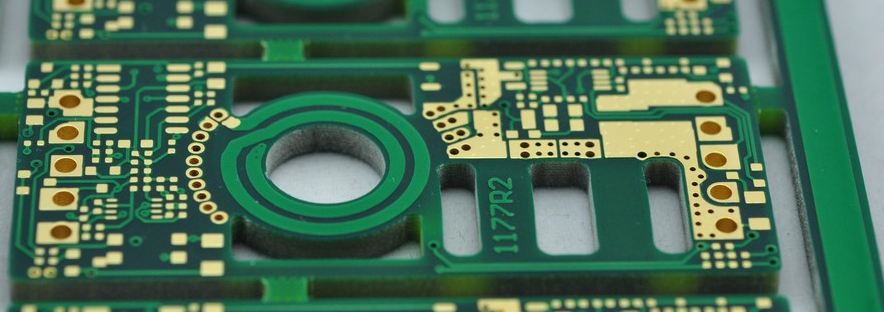
3. ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold)
Principle
ENIG involves depositing a layer of nickel followed by a thin layer of gold on the copper surface. This provides a robust barrier against corrosion and ensures good solderability.
Features
â¢Material: Nickel and gold.
â¢Process: Electroless nickel deposition followed by immersion gold plating.
Advantages
â¢High reliability.
â¢Excellent solderability.
â¢Long shelf life.
Picture
4. ENEPIG (Electroless Nickel Electroless Palladium Immersion Gold)
Principle
ENEPIG is similar to ENIG but adds a palladium layer between the nickel and gold. This improves the resistance to wear and tear.
Features
â¢Material: Nickel, palladium, and gold.
â¢Process: Electroless nickel deposition, electroless palladium, and immersion gold plating.
Advantages
â¢Superior wear resistance.
â¢Excellent solderability.
â¢Long-term reliability.
Applications
â¢High-reliability military and aerospace applications.
â¢High-frequency applications.
â¢Wire bonding
Picture
5. Gold Immersion (Direct Gold Plating)
Principle
Gold immersion directly deposits a layer of gold onto the copper surface without a nickel underlayer.
Features
â¢Material: Gold.
â¢Process: Direct gold plating.
Advantages
â¢High conductivity.
â¢Excellent solderability.
- Silver Immersion
Principle
Silver immersion involves depositing a layer of silver onto the copper surface.
Features
â¢Material: Silver.
â¢Process: Immersion silver plating.
Advantages
â¢High conductivity.
â¢Low cost compared to gold.
Picture
6. Hard Gold (Selective Gold Plating)
Principle
Hard gold is a thicker and harder layer of gold, typically applied selectively to contact areas.
Features
â¢Material: Gold.
â¢Process: Selective gold plating.
Advantages
â¢High wear resistance.
â¢Good electrical contact properties.
Picture
7. Tin Immersion
Principle
Tin immersion deposits a layer of tin onto the copper surface.
Features
â¢Material: Tin.
â¢Process: Immersion tin plating.
Advantages
â¢Good solderability.
â¢Low cost.
Applications
â¢Cost-sensitive applications.
â¢General-purpose electronics.
Picture
Choosing the right surface treatment for your PCB depends on several factors, including the application environment, cost considerations, and performance requirements. Each treatment has its own set of advantages and limitations. Understanding these treatments will help you make informed decisions that enhance the performance and longevity of your electronic devices.
I hope this guide helps you understand the different surface treatments used in PCB manufacturing and their applications. If you have any questions or need further clarification, feel free to reach out!