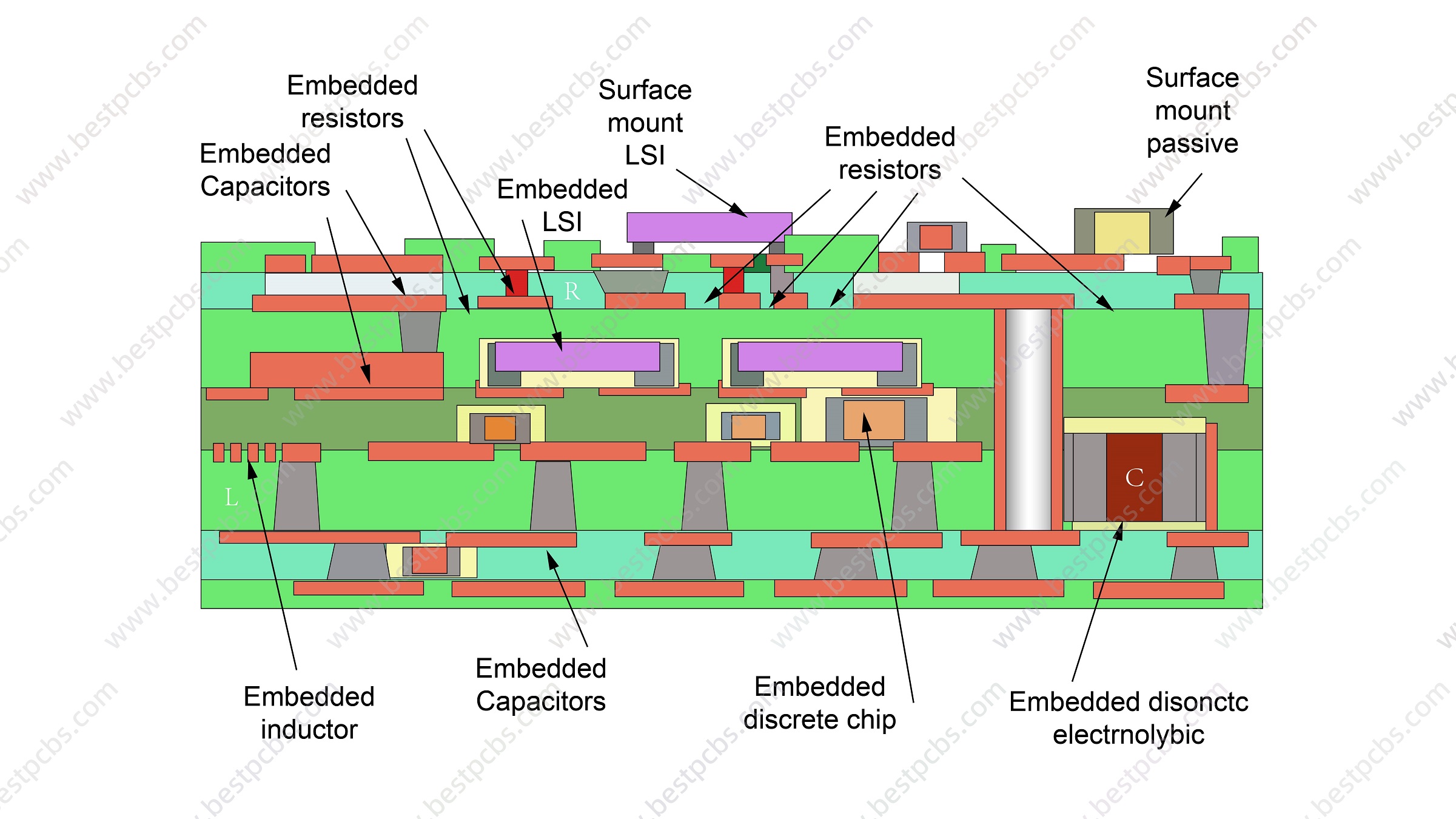
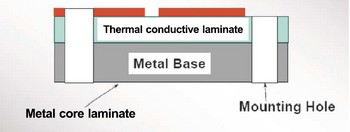
Gold plating is a common surface finish in PCB manufacturing, also known as nickel gold electroplating. It provides excellent conductivity, corrosion resistance and good durability to electronic devices. However, not all gold plating is created equal. There are two primary types of gold plating are used in PCB fabricating: hard gold plating and soft gold plating. They differ in properties, manufacturing process and applications, letās explore it today!
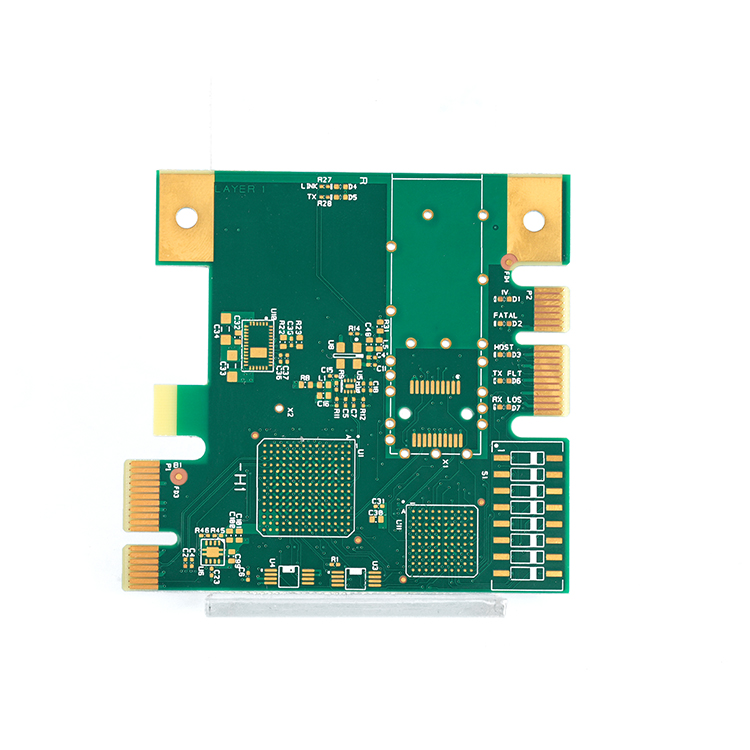
What are Hard Gold Plating and Soft Gold Plating?
In the manufacturing process of printed circuit boards (PCBs), we often hear the words “soft gold” and “hard gold”. They are actually describing the different metal materials used in the gold-plating process.
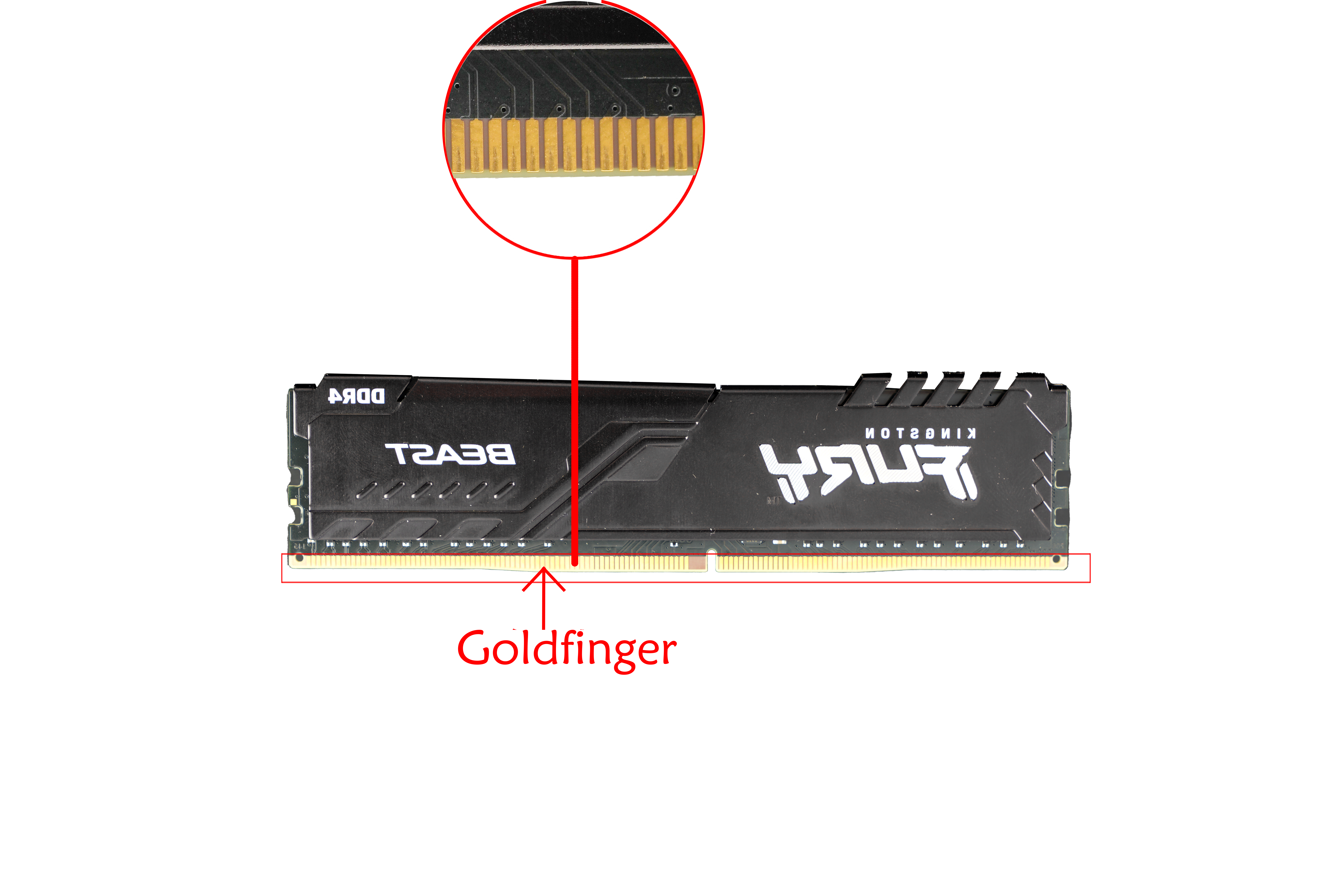
Hard gold usually refers to an alloy formed by electroplating process. This alloy is doped with other metal elements, such as nickel, cobalt, etc., to make it harder and more resistant to friction. Hard gold is especially suitable for places that require force and friction, such as the edge contact points of circuit boards (commonly known as “gold fingers”), because it can withstand frequent insertion and removal operations. Although the processing process of hard gold is complex, it can be doped with other metals to improve the hardness of gold, making it more suitable for making hollow jewelry or for industrial applications.
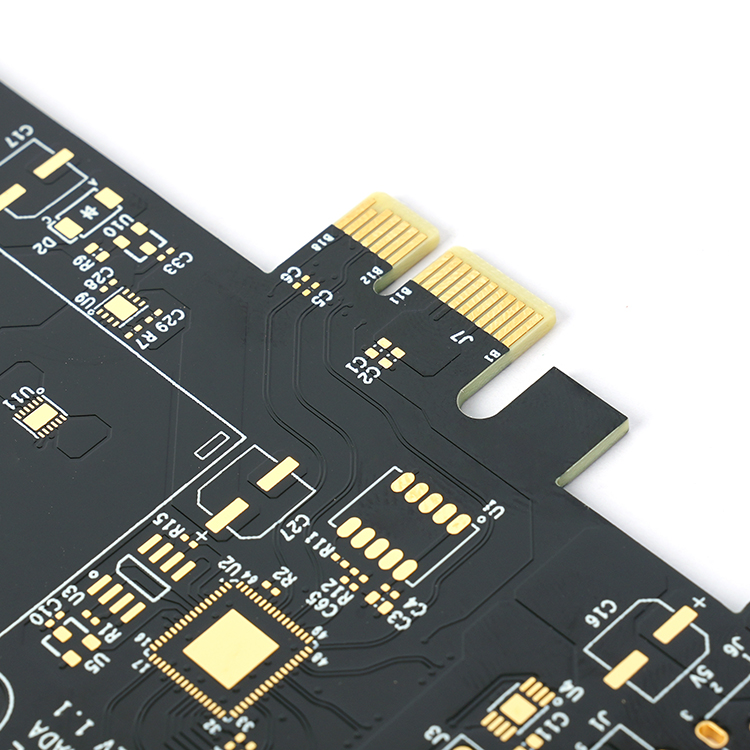
Soft gold refers to the state of pure gold or close to pure gold, because of the high purity of gold, it is relatively soft. Soft gold is mainly used for aluminum wire on COB (Chip On Board), or the contact surface of mobile phone keys, because it can maintain good electrical conductivity and weldability. The processing process of soft gold is relatively simple, does not require complex alloying process, and maintains the soft characteristics of gold, which is suitable for the production of solid jewelry or for applications requiring good electrical conductivity.
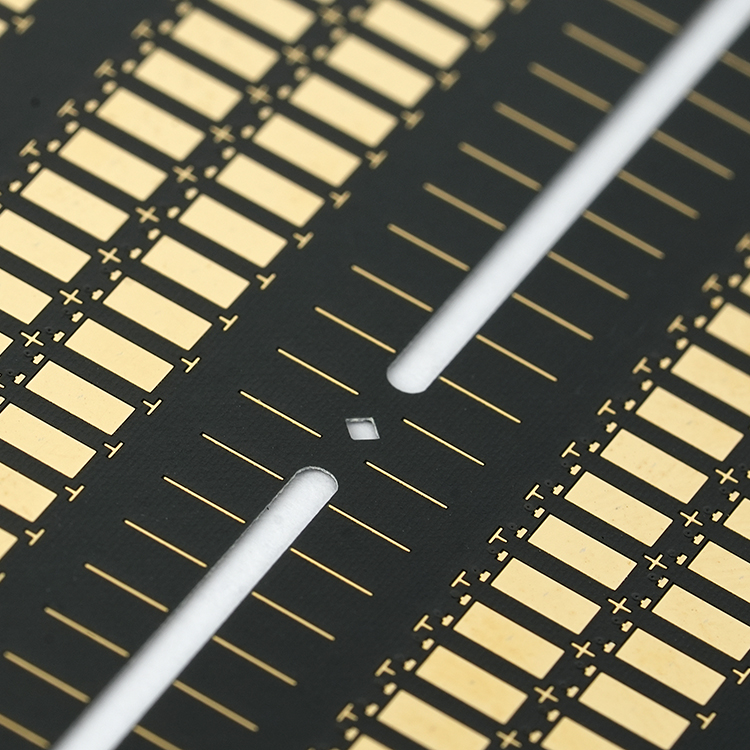
Properties and applications: hard gold plating vs soft gold plating
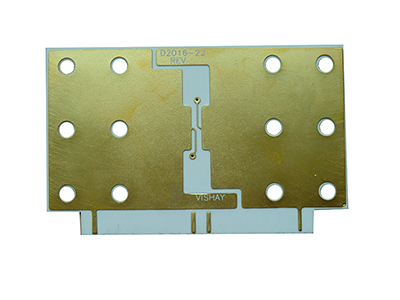
Hard gold plating is known for its high hardness, typically achieved by alloying gold with small amounts of nickel or cobalt. So, it has highly resistant to wear and mechanical stress. The thickness of hard gold plating is usually greater than that of soft gold plating, ranging from 30 to 50uāā or more. Best Technology can make up to 50uāā if you required. Due to the hardness of the hard gold plating, they are commonly used in edge connectors, keypads, and contact points where repeated mechanical action occurs.
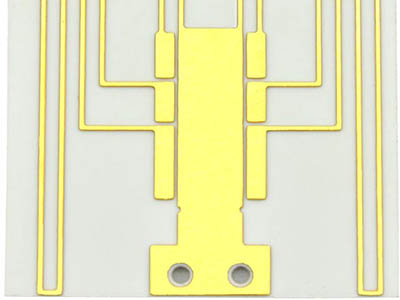
The manufacturing process of soft gold plating involves a chemical process to deposit a thinner layer of pure gold onto the PCB surface. The coated pure gold without any alloying elements, resulting in a softer finished compared to the hard gold plating. Additionally, the thickness of soft gold plating is typically thinner than that of hard gold plating, usually around 1 to 3uāā. Due to the softness and conductivity properties, the soft gold plating technology is often used in applications requiring high conductivity and precision, such as wire bonding and fine-pitch components in high-frequency and high-speed circuits.
Whatās the difference between gold plating and immersion gold?
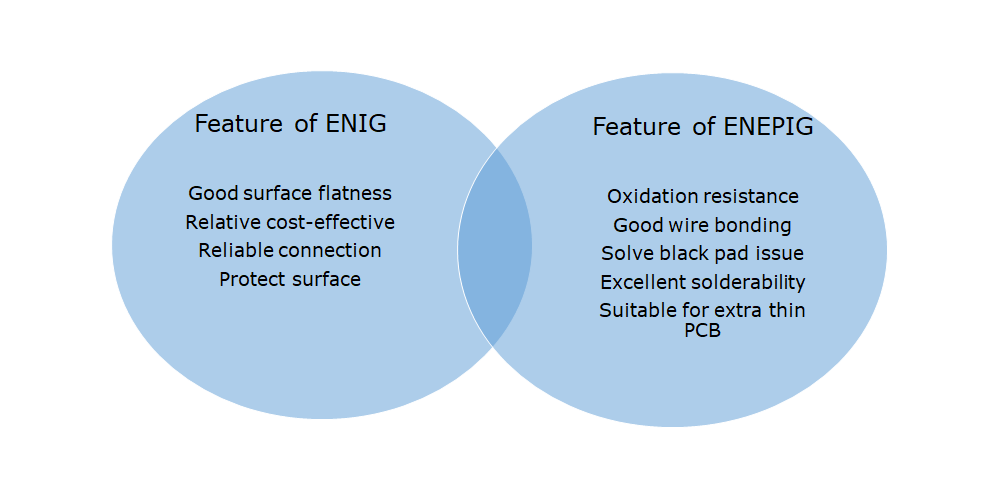
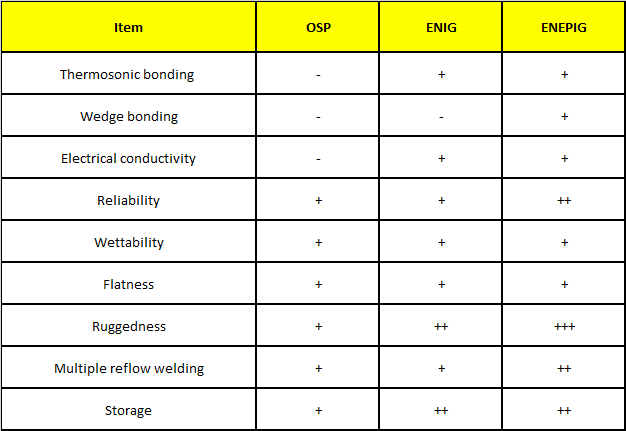
Actually, Immersion Gold is mostly called ENIG (electroless nickel immersion gold) surface treatment method. The advantage of this method is that nickel and gold can be attached to copper without electroplating process, and its surface is smoother than gold plating, which is especially important for the shrinking electronic parts and components requiring flatness.
The method of leaching gold is chemical deposition. A coating is formed by chemical redox reaction, which is generally thick. Electroplating gold is based on the principle of electrolysis, also known as electroplating. Most other metal surface treatments are electroplating. In actual product applications, 90% of the gold PCB board is dipped in gold, because the poor weldability of the electric gold-plated board is its fatal defect.

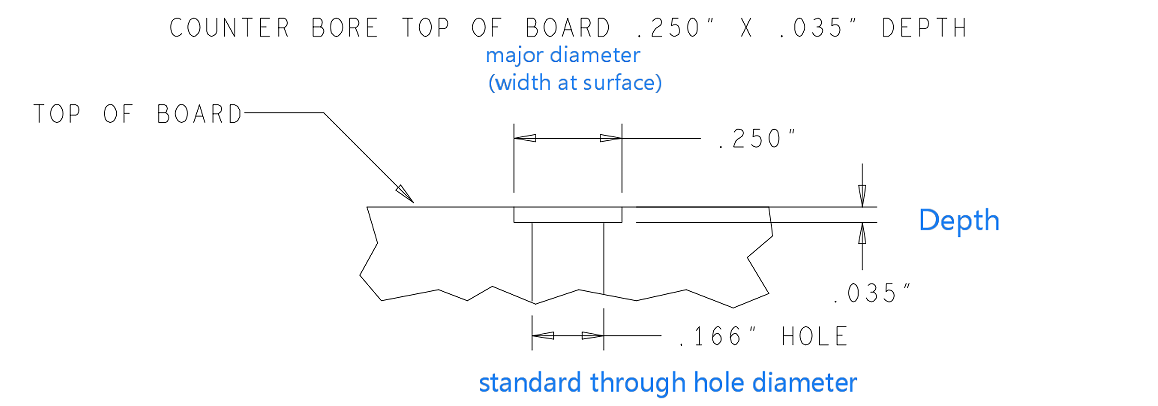
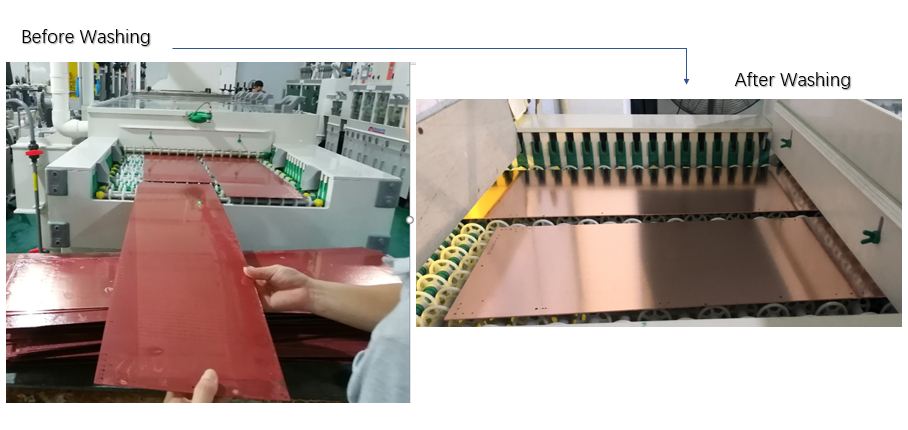
Nickel gold coating with stable color, good brightness, smooth coating and good weldability can be deposited on the surface of printed circuit by gold leaching process. It can be divided into four stages: pretreatment (degreasing, micro-etching, activation, post-leaching), nickel plating, gold leaching, post-treatment (waste gold washing, DI washing, drying). The thickness of gold leaching is 0.025-0.1um. Gold is used in the surface treatment of the circuit board because gold has strong electrical conductivity, good oxidation resistance and long service life. General applications such as keyboard board, gold finger board, etc.
Choosing between hard gold plating and soft gold plating for your PCB depends on your specific application requirements. At Best Technology, we offer expert guidance and high-quality PCB manufacturing services to help you select the best surface finish for your needs. Choose us as your trusted PCB supplier to ensure reliable and efficient solutions for all your electronic projects.