A zero PCB, also known as a prototype PCB or breadboard, is a type of circuit board used for building and testing prototypes. Unlike traditional PCBs, which have pre-defined paths for electric connections, zero PCBs offer a grid of holes. This grid allows for custom circuit designs using wires and components. Engineers and hobbyists use zero PCBs to experiment and develop new electronic circuits without committing to a specific design.
What is a zero PCB?
Zero PCBs are particularly helpful in testing circuit designs for any shortcomings. They provide a cost-efficient way to evaluate the circuitry before committing to a final solution. The term ‘zero’ in this context signifies a fundamental distinction. It implies that there are no predefined connections, layouts, or functions on the PCB.
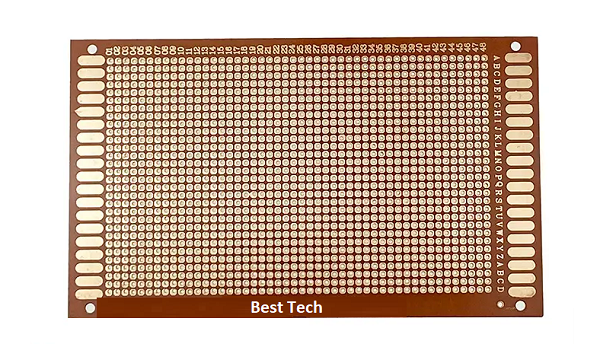
Generally, there is no solder mask and silkscreen on the zero board. The primary purpose of a zero PCB is to offer a blank canvas for users to create and test custom circuits. As a result, they are intentionally kept simple in structure to allow for maximum customization. Users are free to design and solder their circuits and components directly onto the board without the constraints of a predefined layout or solder mask.
What is the use of a zero board?
Zero boards serve a variety of purposes in the electronics industry. They are particularly useful for prototyping and testing new circuit designs. Here are some common uses:
- Prototyping
- Educational purposes
- Quick fixes
- Small-scale production
Zero PCBs have a layer of copper traces or pads on the substrate. These copper elements provide the conductive pathways for soldering electronic components and forming connections. However, the copper traces on zero PCBs are usually unconnected, meaning there is no predefined circuit layout. You can build a circuit on them by inserting components into the holes and then connecting them with wires.
What is the cost of a zero PCB board?
The cost of zero PCB boards varies based on size, material, and supplier. Generally, they are quite cost-effective, so that both professional engineers and hobbyists can afford it. Prices can range from a few cents for small boards to several dollars for larger or more specialized versions. Bulk purchasing often reduces the cost per unit. Additionally, different materials, such as fiberglass or phenolic, can affect the price.
What size is a zero PCB board?
Zero PCB boards come in various sizes to accommodate different project needs. Common sizes include:
- Small: Typically around 5×7 cm, ideal for simple projects.
- Medium: Sizes like 10×15 cm offer more space for complex circuits.
- Large: Boards as large as 30×30 cm are available for extensive projects.
The grid pattern usually remains consistent, with a standard pitch of 2.54 mm (0.1 inches) between holes, regardless of the board’s overall size.
What is a bare board?
A bare board, also known as a blank PCB, is a printed circuit board that has not yet been populated with any electronic components. It is essentially the foundation of a PCB, consisting only of the substrate material (such as fiberglass) and the copper traces that form the circuit pathways. A bare board typically include base core, prepreg and copper trace layer.
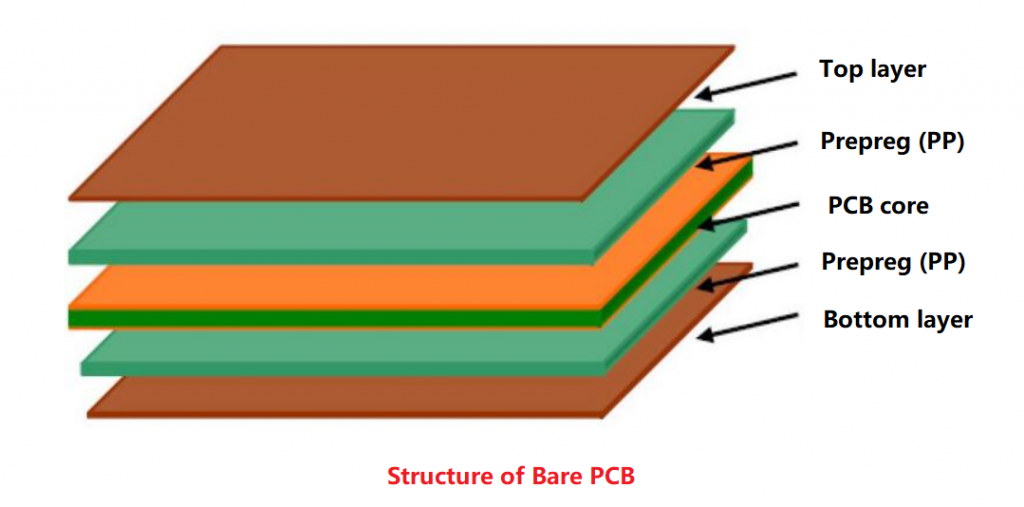
Features of a bare board
- Substrate material
The base material of a bare board is usually fiberglass, FR4, or other insulating materials that provide mechanical support.
- Copper traces
These are the conductive pathways etched onto the substrate. They form the circuit’s electrical connections but are not yet connected to any components.
- Pads and holes
Bare boards include pads (flat areas of copper for soldering components) and drilled holes for through-hole components.
- Pre-defined layout
The copper traces and pads are arranged according to a specific design, determined during the PCB design process.
- No components
A bare board does not have any electronic components soldered onto it yet. It is essentially a “blank slate” ready to be populated.
- Coated solder mask and silkscreen
Most bare boards have a solder mask, a protective layer that prevents solder from bridging between conductive areas, and a silkscreen, which provides component labels and other information.
If you are looking for a reliable supplier for your PCB needs, consider companies like Best Technology, who is known for their quality and customer service. Best Technology offers a range of options to support your electronic projects from prototyping to production. Contact us right now to get your quotation.